Measuring the Impact of Blockchain and Smart Contract on Construction Supply Chain Visibility
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2021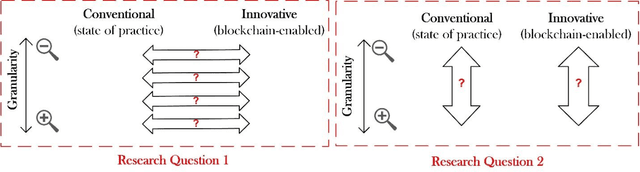

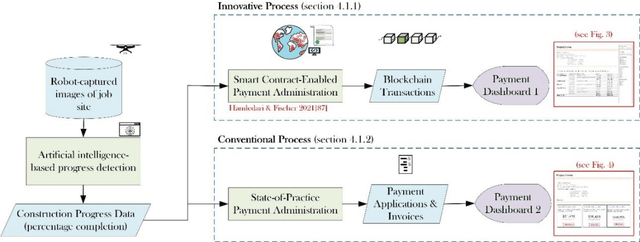

This work assesses the impact of blockchain and smart contract on the visibility of construction supply chain and in the context of payments (intersection of cash and product flows). It uses comparative empirical experiments (Charrette Test Method) to draw comparisons between the visibility of state-of-practice and blockchain-enabled payment systems in a commercial construction project. Comparisons were drawn across four levels of granularity. The findings are twofold: 1) blockchain improved information completeness and information accuracy respectively by an average 216% and 261% compared with the digital state-of-practice solution. The improvements were significantly more pronounced for inquiries that had higher product, trade, and temporal granularity; 2) blockchain-enabled solution was robust in the face of increased granularity, while the conventional solution experienced 50% and 66.7% decline respectively in completeness and accuracy of information. The paper concludes with a discussion of mechanisms contributing to visibility and technology adoption based on business objectives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge