Measuring Inter-group Agreement on zSlice Based General Type-2 Fuzzy Sets
Paper and Code
Jul 09, 2019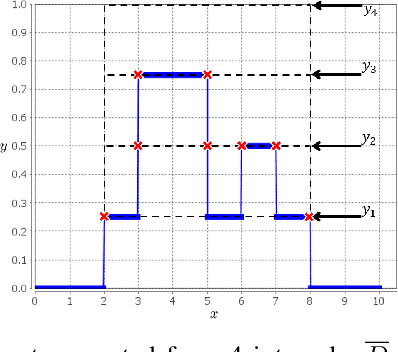

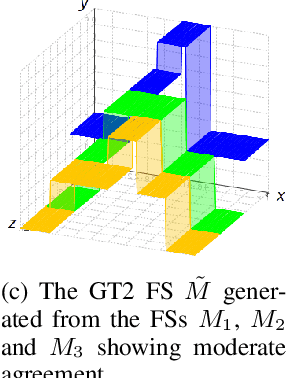
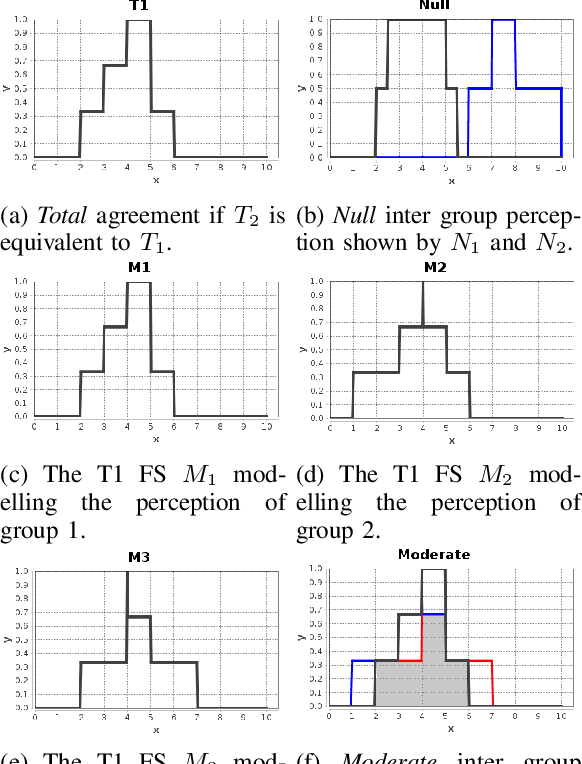
Recently, there has been much research into modelling of uncertainty in human perception through Fuzzy Sets (FSs). Most of this research has focused on allowing respondents to express their (intra) uncertainty using intervals. Here, depending on the technique used and types of uncertainties being modelled different types of FSs can be obtained (e.g., Type-1, Interval Type-2, General Type-2). Arguably, one of the most flexible techniques is the Interval Agreement Approach (IAA) as it allows to model the perception of all respondents without making assumptions such as outlier removal or predefined membership function types (e.g. Gaussian). A key aspect in the analysis of interval-valued data and indeed, IAA based agreement models of said data, is to determine the position and strengths of agreement across all the sources/participants. While previously, the Agreement Ratio was proposed to measure the strength of agreement in fuzzy set based models of interval data, said measure has only been applicable to type-1 fuzzy sets. In this paper, we extend the Agreement Ratio to capture the degree of inter-group agreement modelled by a General Type-2 Fuzzy Set when using the IAA. This measure relies on using a similarity measure to quantitatively express the relation between the different levels of agreement in a given FS. Synthetic examples are provided in order to demonstrate both behaviour and calculation of the measure. Finally, an application to real-world data is provided in order to show the potential of this measure to assess the divergence of opinions for ambiguous concepts when heterogeneous groups of participants are involved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge