Maximum sampled conditional likelihood for informative subsampling
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2020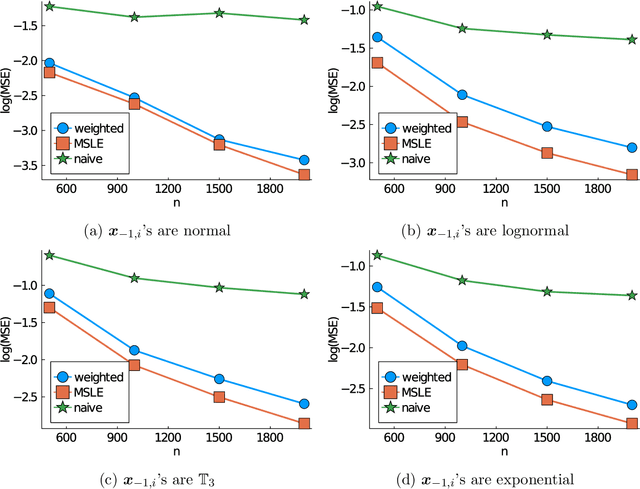
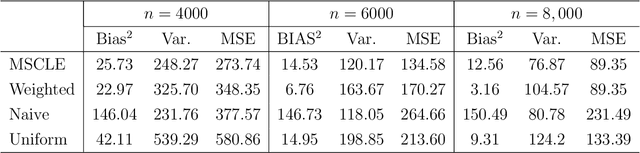
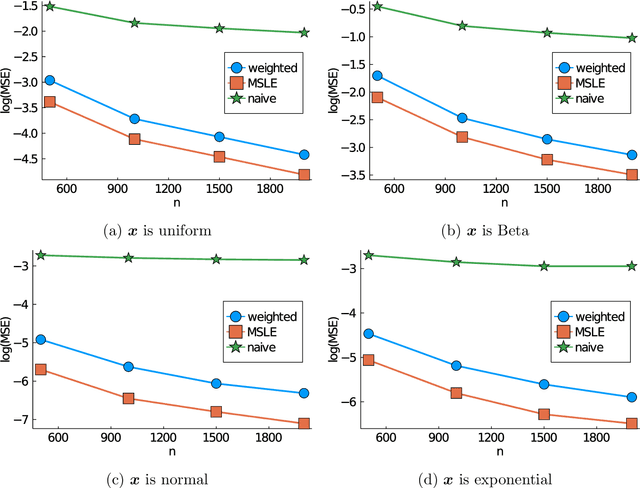
Subsampling is a computationally effective approach to extract information from massive data sets when computing resources are limited. After a subsample is taken from the full data, most available methods use an inverse probability weighted objective function to estimate the model parameters. This type of weighted estimator does not fully utilize information in the selected subsample. In this paper, we propose to use the maximum sampled conditional likelihood estimator (MSCLE) based on the sampled data. We established the asymptotic normality of the MSCLE and prove that its asymptotic variance covariance matrix is the smallest among a class of asymptotically unbiased estimators, including the inverse probability weighted estimator. We further discuss the asymptotic results with the L-optimal subsampling probabilities and illustrate the estimation procedure with generalized linear models. Numerical experiments are provided to evaluate the practical performance of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge