Maximal Jacobian-based Saliency Map Attack
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2018
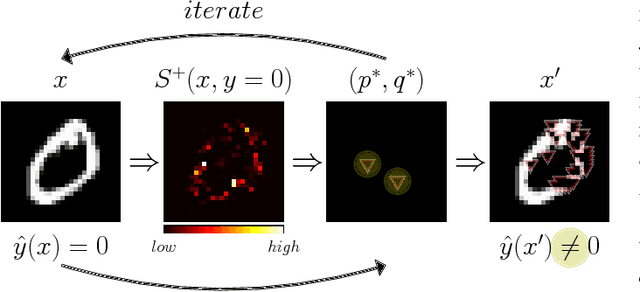

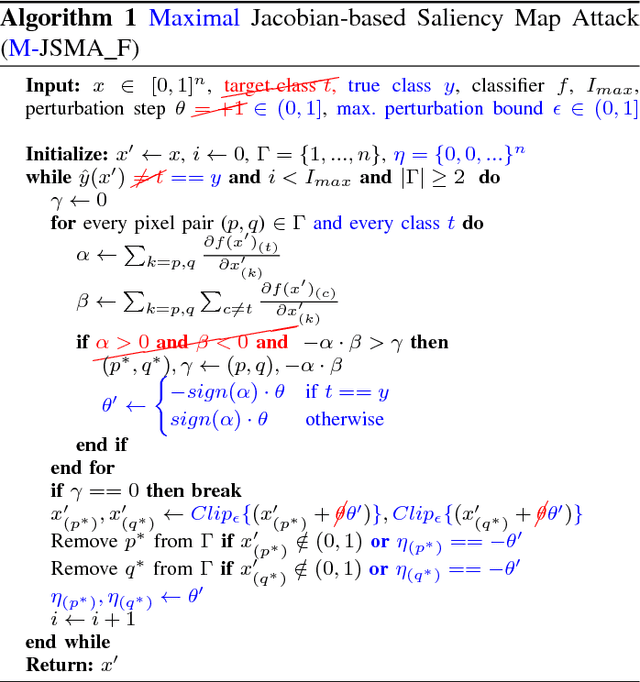
The Jacobian-based Saliency Map Attack is a family of adversarial attack methods for fooling classification models, such as deep neural networks for image classification tasks. By saturating a few pixels in a given image to their maximum or minimum values, JSMA can cause the model to misclassify the resulting adversarial image as a specified erroneous target class. We propose two variants of JSMA, one which removes the requirement to specify a target class, and another that additionally does not need to specify whether to only increase or decrease pixel intensities. Our experiments highlight the competitive speeds and qualities of these variants when applied to datasets of hand-written digits and natural scenes.
* Extended version of extended abstract for MAIS 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge