Masking Effects in Combined Hardness and Stiffness Rendering Using an Encountered-Type Haptic Display
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2021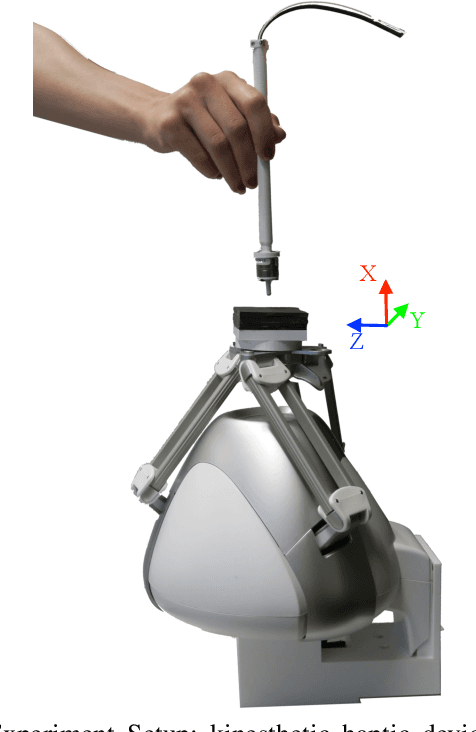



Rendering stable hard surfaces is an important problem in haptics for many tasks, including training simulators for orthopedic surgery or dentistry. Current impedance devices cannot provide enough force and stiffness to render a wall, and the high friction and inertia of admittance devices make it difficult to render free space. We propose to address these limitations by combining haptic augmented reality, untethered haptic interaction, and an encountered-type haptic display. We attach a plate with the desired hardness on the kinesthetic device's end-effector, which the user interacts with using an untethered stylus. This method allows us to directly change the hardness of the end-effector based on the rendered object. In this paper, we evaluate how changing the hardness of the end-effector can mask the device's stiffness and affect the user's perception. The results of our human subject experiment indicate that when the end-effector is made of a hard material, it is difficult for users to perceive when the underlying stiffness being rendered by the device is changed, but this stiffness change is easy to distinguish while the end-effector is made of a soft material. These results show promise for our approach in avoiding the limitations of haptic devices when rendering hard surfaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge