Magnitude or Phase? A Two Stage Algorithm for Dereverberation
Paper and Code
Oct 31, 2022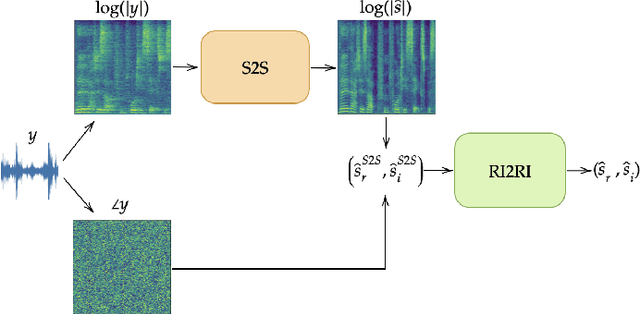



In this work we present a new single-microphone speech dereverberation algorithm. First, a performance analysis is presented to interpret that algorithms focused on improving solely magnitude or phase are not good enough. Furthermore, we demonstrate that few objective measurements have high correlation with the clean magnitude while others with the clean phase. Consequently ,we propose a new architecture which consists of two sub-models, each of which is responsible for a different task. The first model estimates the clean magnitude given the noisy input. The enhanced magnitude together with the noisy-input phase are then used as inputs to the second model to estimate the real and imaginary portions of the dereverberated signal. A training scheme including pre-training and fine-tuning is presented in the paper. We evaluate our proposed approach using data from the REVERB challenge and compare our results to other methods. We demonstrate consistent improvements in all measures, which can be attributed to the improved estimates of both the magnitude and the phase.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge