Machine Learning for Touch Localization on Ultrasonic Wave Touchscreen
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2022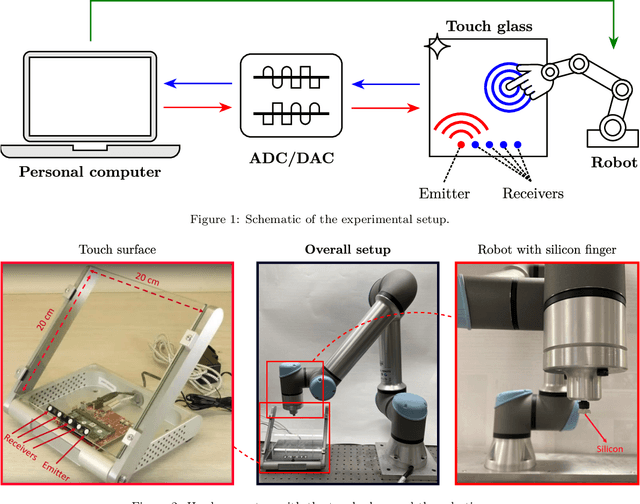
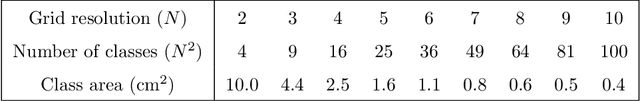
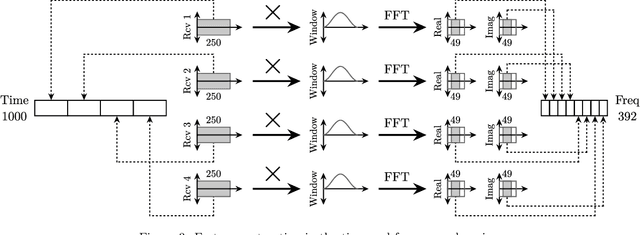
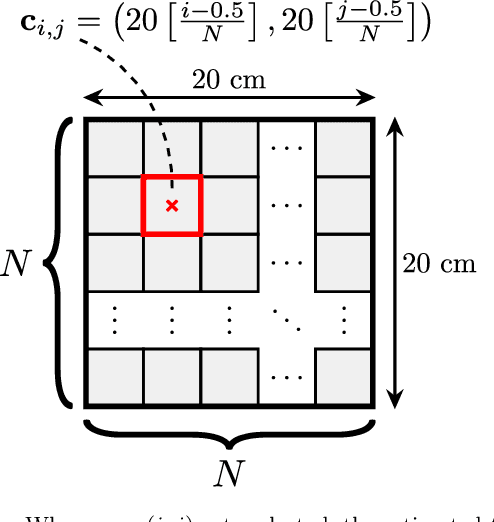
Classification and regression employing a simple Deep Neural Network (DNN) are investigated to perform touch localization on a tactile surface using ultrasonic guided waves. A model is trained using data captured using a robotic finger, and validated with experiments conducted with human fingers. The proposed method provides satisfactory localization results for most human-machine interactions, with a mean error of 0.47 cm and standard deviation of 0.18 cm. The classification approach is also adapted to identify touches on an access control keypad layout, which leads to an accuracy of 97%. These results demonstrate that DNN-based methods are a viable alternative to signal processing-based approaches for accurate and robust touch localization using ultrasonic guided waves.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge