Machine Learning for Antimicrobial Resistance
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2016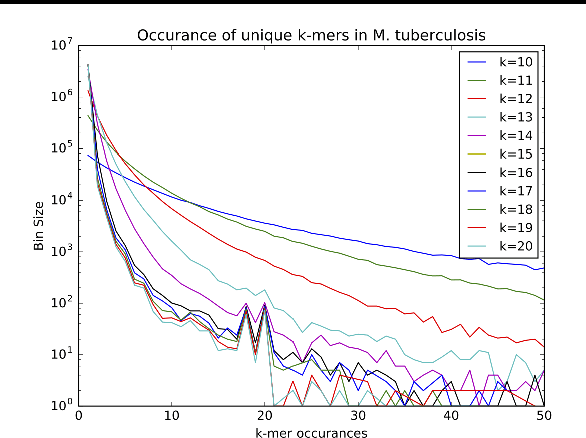
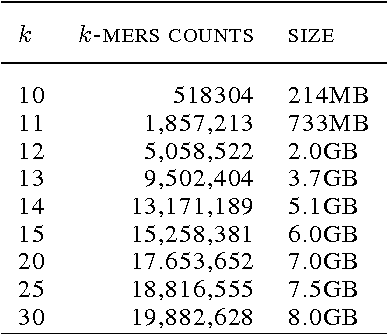
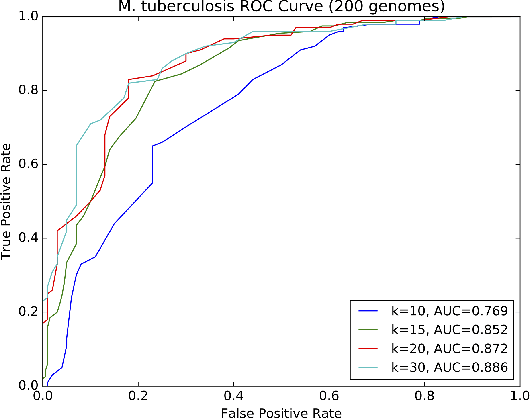
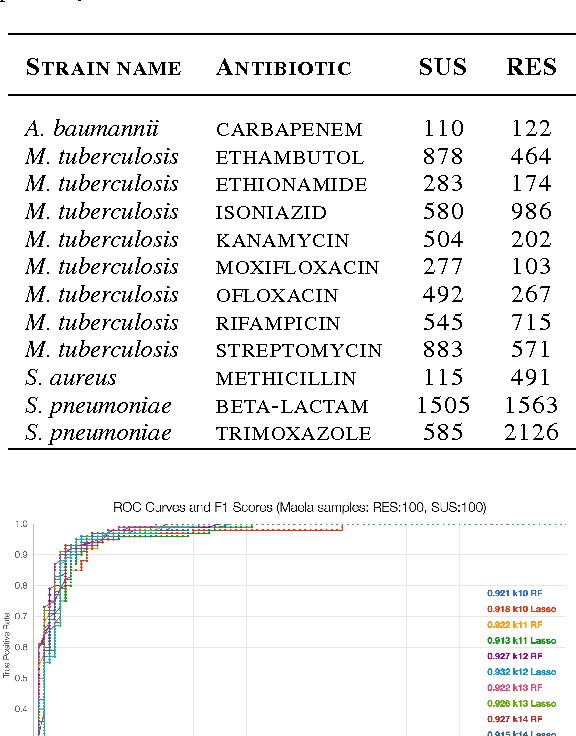
Biological datasets amenable to applied machine learning are more available today than ever before, yet they lack adequate representation in the Data-for-Good community. Here we present a work in progress case study performing analysis on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) using standard ensemble machine learning techniques and note the successes and pitfalls such work entails. Broadly, applied machine learning (AML) techniques are well suited to AMR, with classification accuracies ranging from mid-90% to low- 80% depending on sample size. Additionally, these techniques prove successful at identifying gene regions known to be associated with the AMR phenotype. We believe that the extensive amount of biological data available, the plethora of problems presented, and the global impact of such work merits the consideration of the Data- for-Good community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge