Low-Cost Inertial Aiding for Deep-Urban Tightly-Coupled Multi-Antenna Precise GNSS
Paper and Code
Jan 27, 2022
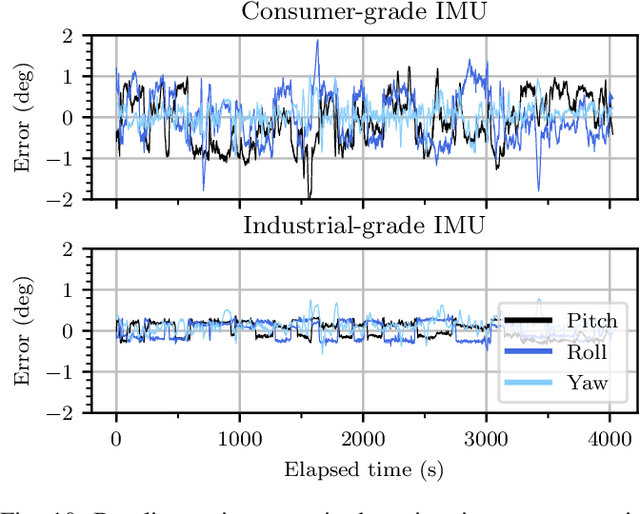
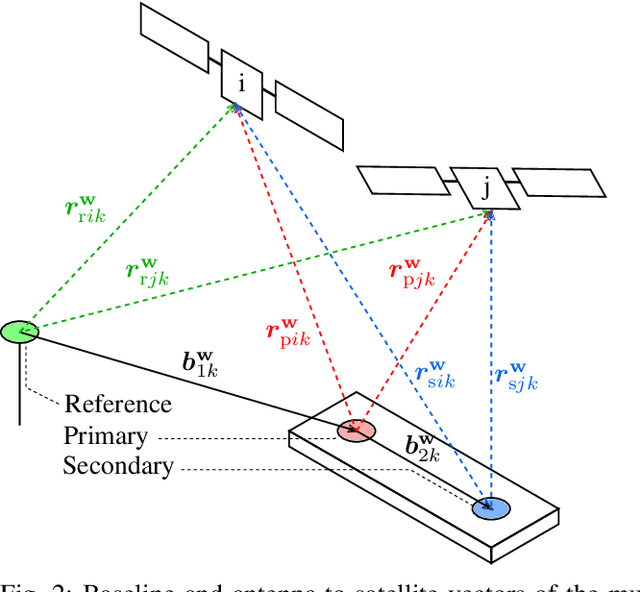
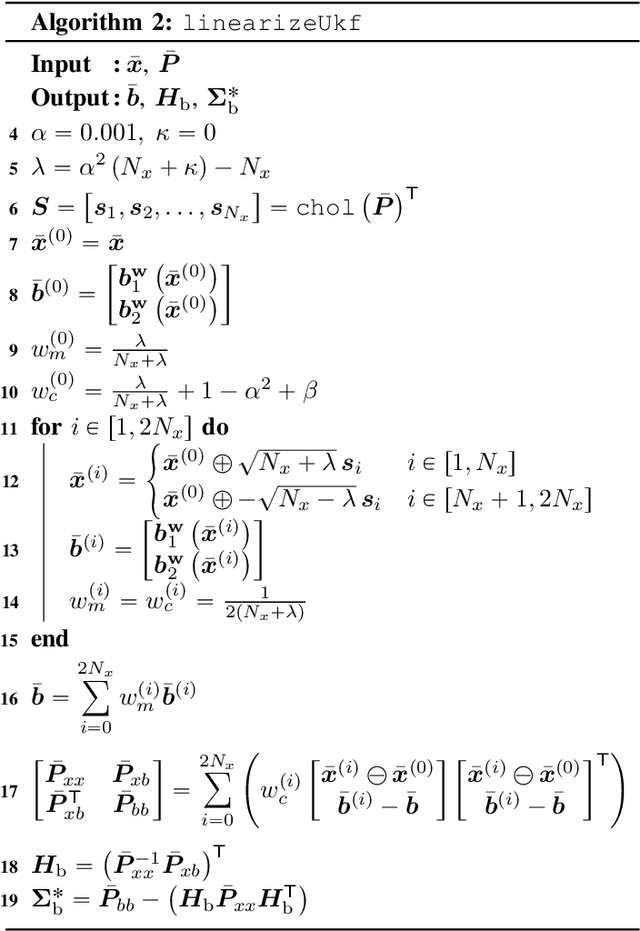
A vehicular pose estimation technique is presented that tightly couples multi-antenna carrier-phase differential GNSS (CDGNSS) with a low-cost MEMS inertial sensor and vehicle dynamics constraints. This work is the first to explore the use of consumer-grade inertial sensors for tightly-coupled urban CDGNSS, and first to explore the tightly-coupled combination of multi-antenna CDGNSS and inertial sensing (of any quality) for urban navigation. An unscented linearization permits ambiguity resolution using traditional integer least squares while both implicitly enforcing known-baseline-length constraints and exploiting the multi-baseline problem's inter-baseline correlations. A novel false fix detection and recovery technique is developed to mitigate the effect of conditioning the filter state on incorrect integers. When evaluated on the publicly-available TEX-CUP urban positioning dataset, the proposed technique achieves, with consumer- and industrial-grade inertial sensors, respectively, a 96.6% and 97.5% integer fix availability, and 12.0 cm and 10.1 cm overall (fix and float) 95th percentile horizontal positioning error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge