Lost in Transmission: On the Impact of Networking Corruptions on Video Machine Learning Models
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2022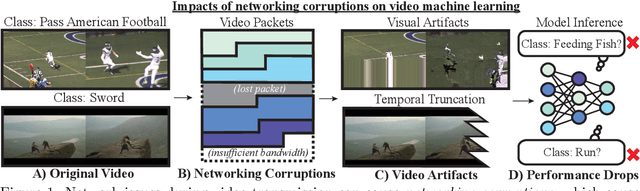
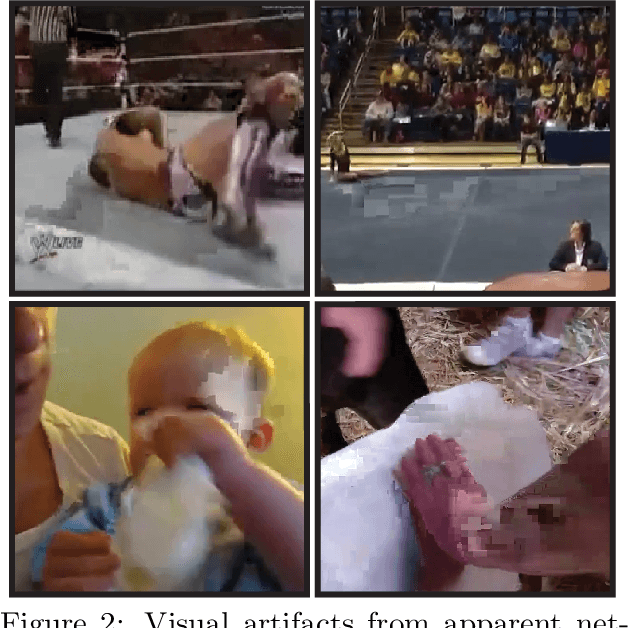
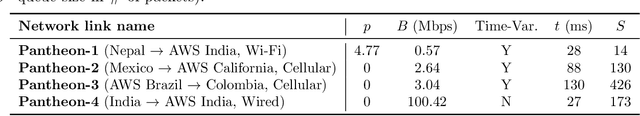


We study how networking corruptions--data corruptions caused by networking errors--affect video machine learning (ML) models. We discover apparent networking corruptions in Kinetics-400, a benchmark video ML dataset. In a simulation study, we investigate (1) what artifacts networking corruptions cause, (2) how such artifacts affect ML models, and (3) whether standard robustness methods can mitigate their negative effects. We find that networking corruptions cause visual and temporal artifacts (i.e., smeared colors or frame drops). These networking corruptions degrade performance on a variety of video ML tasks, but effects vary by task and dataset, depending on how much temporal context the tasks require. Lastly, we evaluate data augmentation--a standard defense for data corruptions--but find that it does not recover performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge