Long-VMNet: Accelerating Long-Form Video Understanding via Fixed Memory
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2025
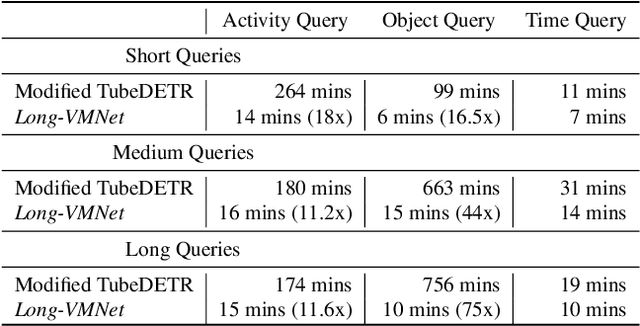
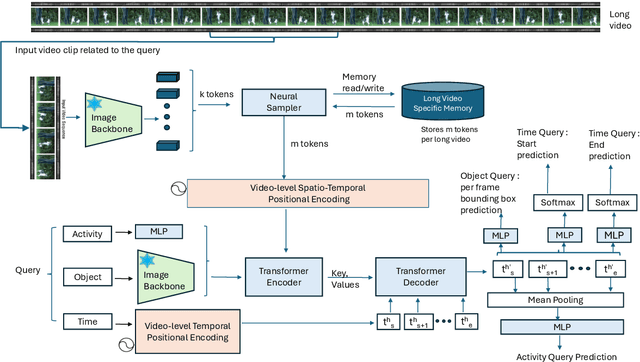
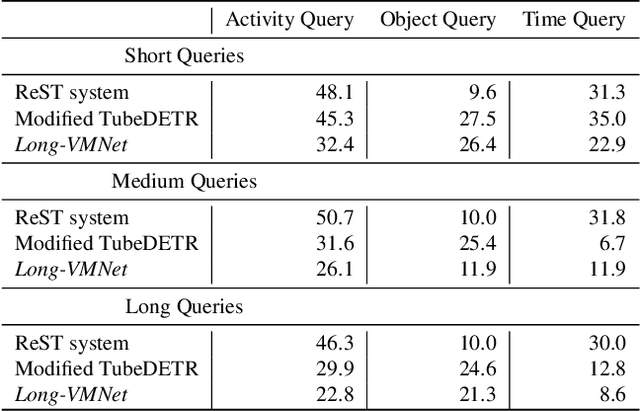
Long-form video understanding is essential for various applications such as video retrieval, summarizing, and question answering. Yet, traditional approaches demand substantial computing power and are often bottlenecked by GPU memory. To tackle this issue, we present Long-Video Memory Network, Long-VMNet, a novel video understanding method that employs a fixed-size memory representation to store discriminative patches sampled from the input video. Long-VMNet achieves improved efficiency by leveraging a neural sampler that identifies discriminative tokens. Additionally, Long-VMNet only needs one scan through the video, greatly boosting efficiency. Our results on the Rest-ADL dataset demonstrate an 18x -- 75x improvement in inference times for long-form video retrieval and answering questions, with a competitive predictive performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge