LLMs as a synthesis between symbolic and continuous approaches to language
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2025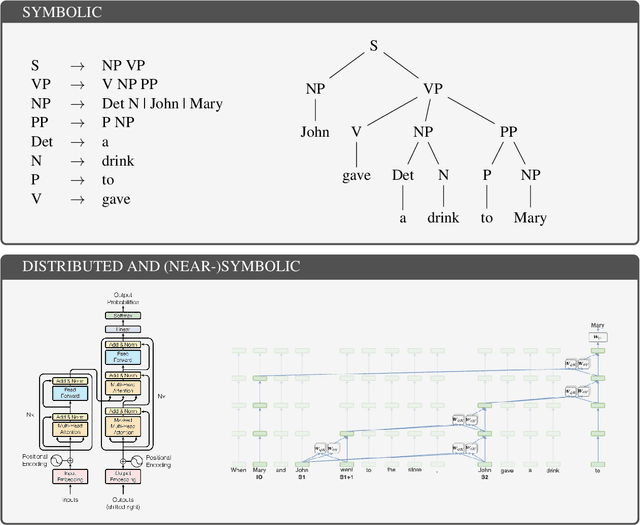
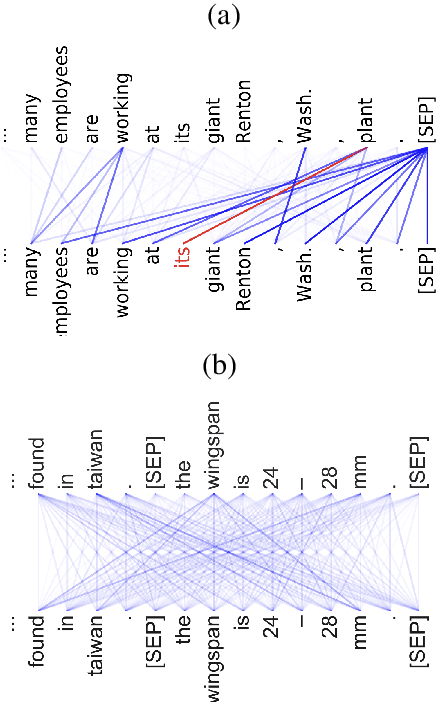
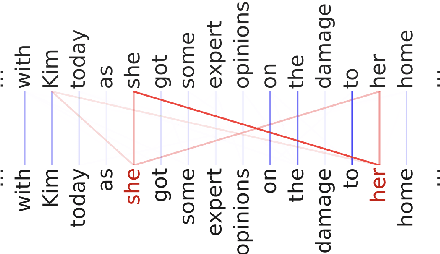
Since the middle of the 20th century, a fierce battle is being fought between symbolic and continuous approaches to language and cognition. The success of deep learning models, and LLMs in particular, has been alternatively taken as showing that the continuous camp has won, or dismissed as an irrelevant engineering development. However, in this position paper I argue that deep learning models for language actually represent a synthesis between the two traditions. This is because 1) deep learning architectures allow for both continuous/distributed and symbolic/discrete-like representations and computations; 2) models trained on language make use this flexibility. In particular, I review recent research in mechanistic interpretability that showcases how a substantial part of morphosyntactic knowledge is encoded in a near-discrete fashion in LLMs. This line of research suggests that different behaviors arise in an emergent fashion, and models flexibly alternate between the two modes (and everything in between) as needed. This is possibly one of the main reasons for their wild success; and it is also what makes them particularly interesting for the study of language and cognition. Is it time for peace?
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge