Linear Scalarization for Byzantine-robust learning on non-IID data
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2022
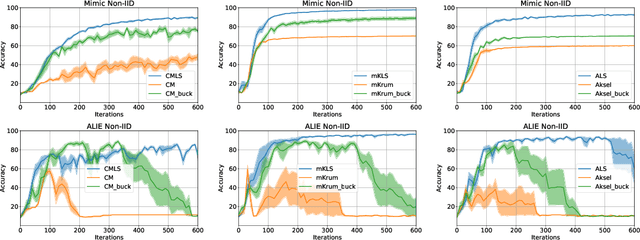
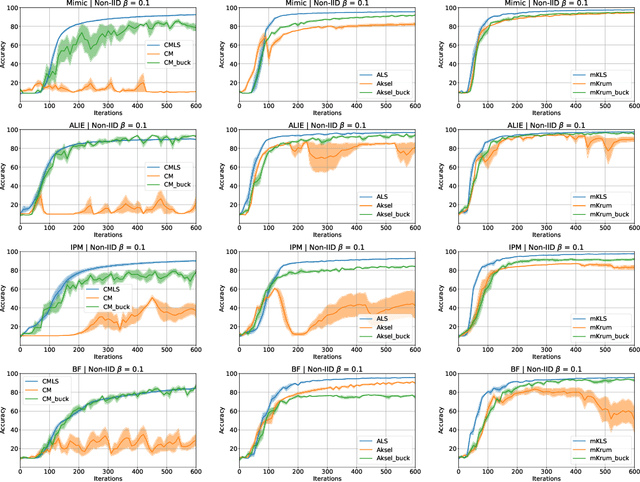
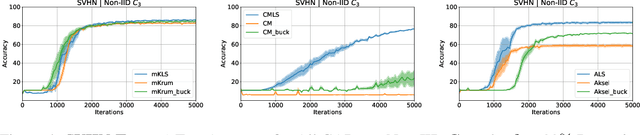
In this work we study the problem of Byzantine-robust learning when data among clients is heterogeneous. We focus on poisoning attacks targeting the convergence of SGD. Although this problem has received great attention; the main Byzantine defenses rely on the IID assumption causing them to fail when data distribution is non-IID even with no attack. We propose the use of Linear Scalarization (LS) as an enhancing method to enable current defenses to circumvent Byzantine attacks in the non-IID setting. The LS method is based on the incorporation of a trade-off vector that penalizes the suspected malicious clients. Empirical analysis corroborates that the proposed LS variants are viable in the IID setting. For mild to strong non-IID data splits, LS is either comparable or outperforming current approaches under state-of-the-art Byzantine attack scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge