Learning Unfair Trading: a Market Manipulation Analysis From the Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Paper and Code
Nov 02, 2015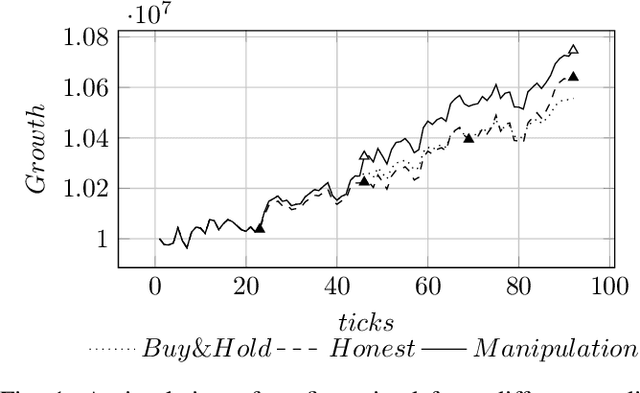
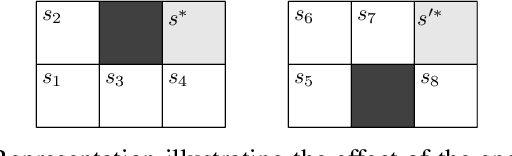
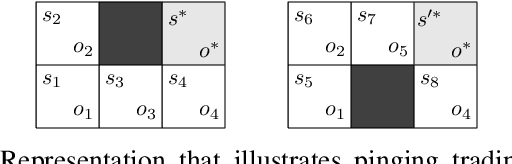
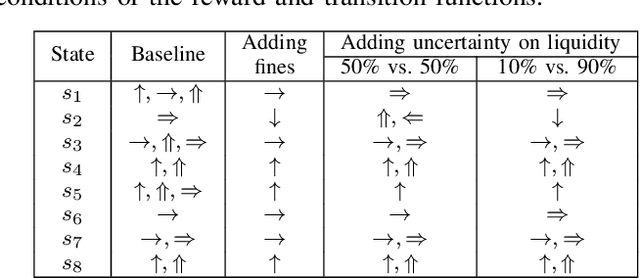
Market manipulation is a strategy used by traders to alter the price of financial securities. One type of manipulation is based on the process of buying or selling assets by using several trading strategies, among them spoofing is a popular strategy and is considered illegal by market regulators. Some promising tools have been developed to detect manipulation, but cases can still be found in the markets. In this paper we model spoofing and pinging trading, two strategies that differ in the legal background but share the same elemental concept of market manipulation. We use a reinforcement learning framework within the full and partial observability of Markov decision processes and analyse the underlying behaviour of the manipulators by finding the causes of what encourages the traders to perform fraudulent activities. This reveals procedures to counter the problem that may be helpful to market regulators as our model predicts the activity of spoofers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge