Learning to Simplify with Data Hopelessly Out of Alignment
Paper and Code
Apr 02, 2022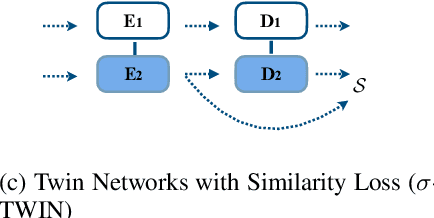

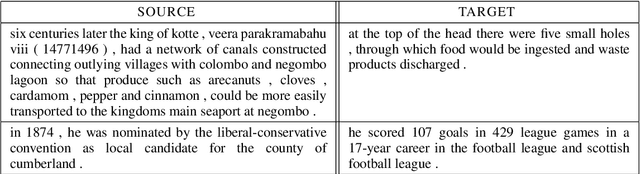
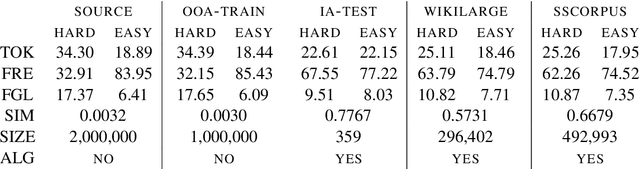
We consider whether it is possible to do text simplification without relying on a "parallel" corpus, one that is made up of sentence-by-sentence alignments of complex and ground truth simple sentences. To this end, we introduce a number of concepts, some new and some not, including what we call Conjoined Twin Networks, Flip-Flop Auto-Encoders (FFA) and Adversarial Networks (GAN). A comparison is made between Jensen-Shannon (JS-GAN) and Wasserstein GAN, to see how they impact performance, with stronger results for the former. An experiment we conducted with a large dataset derived from Wikipedia found the solid superiority of Twin Networks equipped with FFA and JS-GAN, over the current best performing system. Furthermore, we discuss where we stand in a relation to fully supervised methods in the past literature, and highlight with examples qualitative differences that exist among simplified sentences generated by supervision-free systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge