Learning $\textit{Ex Nihilo}$
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2019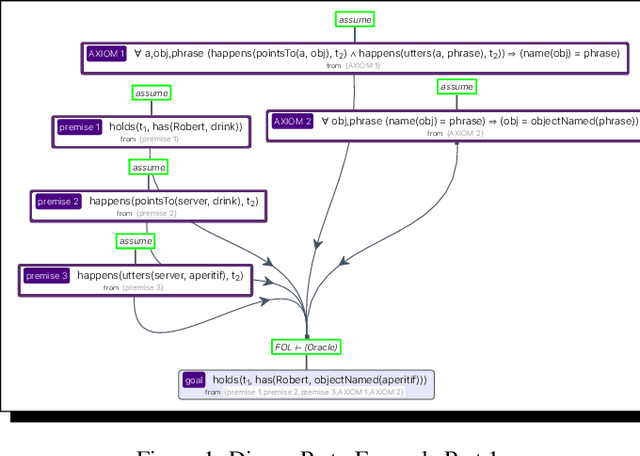
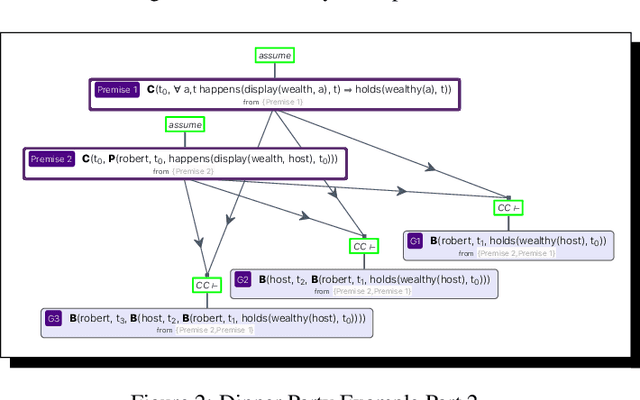
This paper introduces, philosophically and to a degree formally, the novel concept of learning $\textit{ex nihilo}$, intended (obviously) to be analogous to the concept of creation $\textit{ex nihilo}$. Learning $\textit{ex nihilo}$ is an agent's learning "from nothing," by the suitable employment of schemata for deductive and inductive reasoning. This reasoning must be in machine-verifiable accord with a formal proof/argument theory in a $\textit{cognitive calculus}$ (i.e., roughly, an intensional higher-order multi-operator quantified logic), and this reasoning is applied to percepts received by the agent, in the context of both some prior knowledge, and some prior and current interests. Learning $\textit{ex nihilo}$ is a challenge to contemporary forms of ML, indeed a severe one, but the challenge is offered in the spirt of seeking to stimulate attempts, on the part of non-logicist ML researchers and engineers, to collaborate with those in possession of learning-$\textit{ex nihilo}$ frameworks, and eventually attempts to integrate directly with such frameworks at the implementation level. Such integration will require, among other things, the symbiotic interoperation of state-of-the-art automated reasoners and high-expressivity planners, with statistical/connectionist ML technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge