Learning heterophilious edge to drop: A general framework for boosting graph neural networks
Paper and Code
May 23, 2022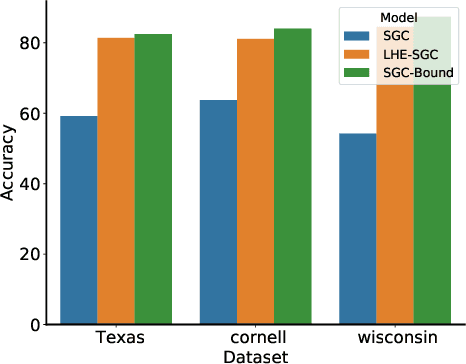
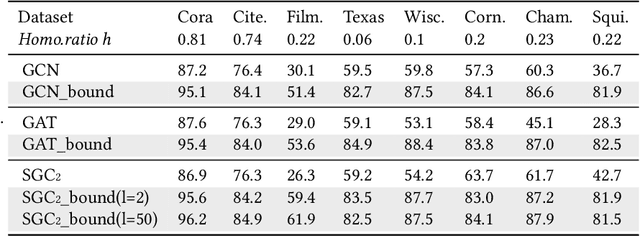


Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) aim at integrating node contents with graph structure to learn nodes/graph representations. Nevertheless, it is found that most of existing GNNs do not work well on data with high heterophily level that accounts for a large proportion of edges between different class labels. Recently, many efforts to tackle this problem focus on optimizing the way of feature learning. From another angle, this work aims at mitigating the negative impacts of heterophily by optimizing graph structure for the first time. Specifically, on assumption that graph smoothing along heterophilious edges can hurt prediction performance, we propose a structure learning method called LHE to identify heterophilious edges to drop. A big advantage of this solution is that it can boost GNNs without careful modification of feature learning strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate the remarkable performance improvement of GNNs with \emph{LHE} on multiple datasets across full spectrum of homophily level.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge