Laser Ranging Based Intelligent System for Unknown Environment Mapping
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2023
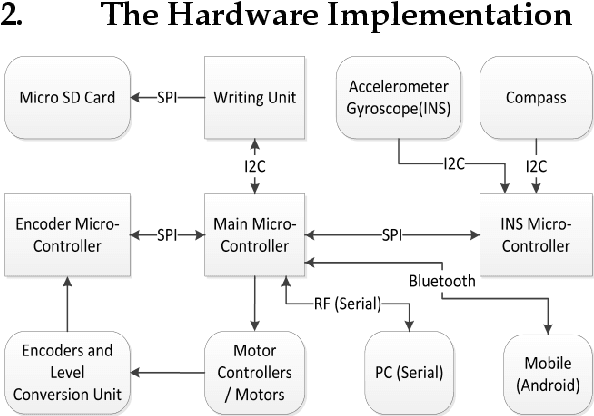
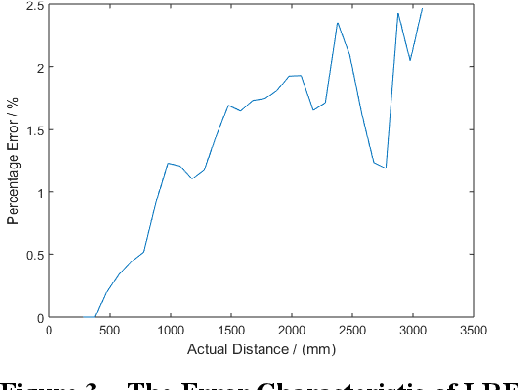
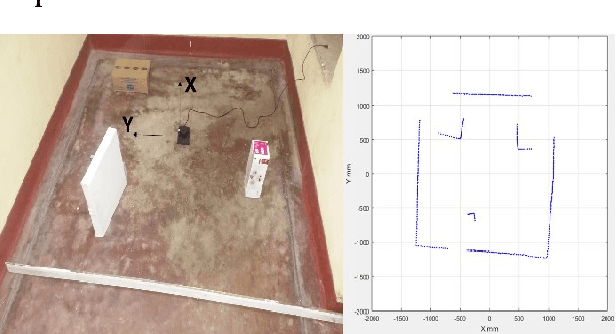
This work describes the implementation of a simple and computationally efficient Intelligent Navigation System (INS) for autonomous systems used in areas where human access is impossible. The system uses Laser Range Finder (LRF) readings as input, making it suitable for mobile platform implementation. The INS pre-processes the LRF readings to remove noise and determines an obstacle-free path for mapping. The system's localization method uses a similarity transform and particle filter. The system was tested in artificially generated environments and emulated in real-time with real-environment data. The system was then implemented in a Raspberry Pi3 on a 3WD Omni-directional mobile platform and tested in real environments. The system was able to generate an accurate 2D map of the area. The proposed methodology was shown to be efficient through a comparative analysis of execution time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge