Laser Inter-Satellite Links in a Starlink Constellation
Paper and Code
Feb 26, 2021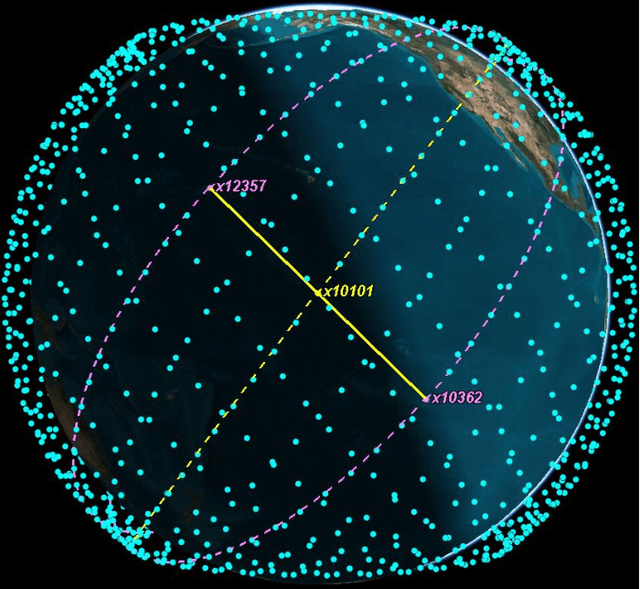



Laser inter-satellite links (LISLs) are envisioned between satellites in upcoming satellite constellations, such as Phase I of SpaceX's Starlink. Within a constellation, satellites can establish LISLs with other satellites in the same orbital plane or in different orbital planes. We present a classification of LISLs based on the location of satellites within a constellation and the duration of LISLs. Then, using satellite constellation for Phase I of Starlink, we study the effect of varying a satellite's LISL range on the number of different types of LISLs it can establish with other satellites. In addition to permanent LISLs, we observe a significant number of temporary LISLs between satellites in crossing orbital planes. Such LISLs can play a vital role in achieving low-latency paths within next-generation optical wireless satellite networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge