Large-Scale Noun Compound Interpretation Using Bootstrapping and the Web as a Corpus
Paper and Code
Nov 27, 2019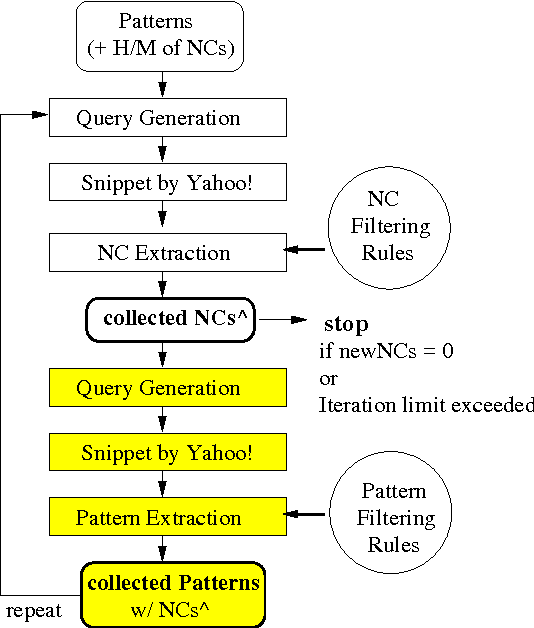

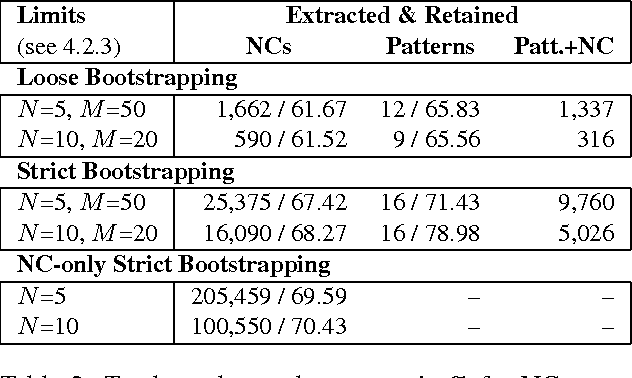
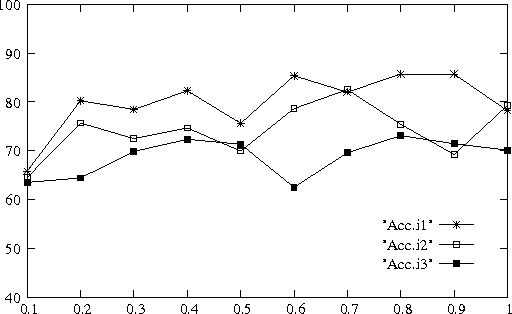
Responding to the need for semantic lexical resources in natural language processing applications, we examine methods to acquire noun compounds (NCs), e.g., "orange juice", together with suitable fine-grained semantic interpretations, e.g., "squeezed from", which are directly usable as paraphrases. We employ bootstrapping and web statistics, and utilize the relationship between NCs and paraphrasing patterns to jointly extract NCs and such patterns in multiple alternating iterations. In evaluation, we found that having one compound noun fixed yields both a higher number of semantically interpreted NCs and improved accuracy due to stronger semantic restrictions.
* EMNLP-2011 * noun compounds, paraphrasing verbs, paraphrases, semantic
interpretation, bootstrapping, semi-supervised learning
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge