Language discrimination and clustering via a neural network approach
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2015
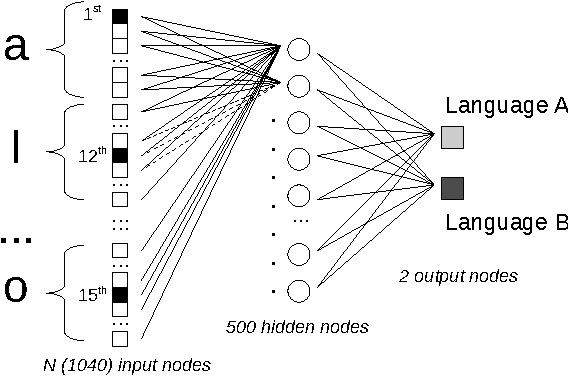
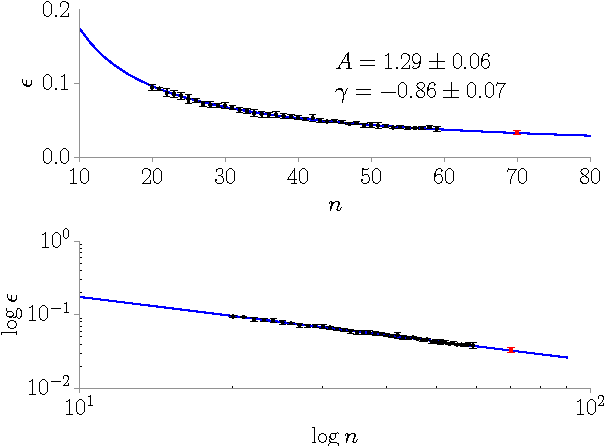
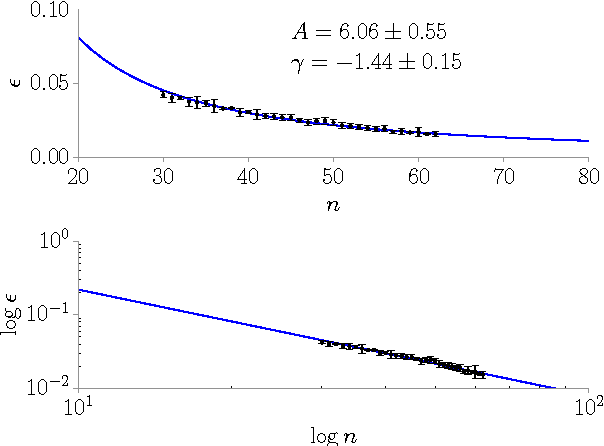
We classify twenty-one Indo-European languages starting from written text. We use neural networks in order to define a distance among different languages, construct a dendrogram and analyze the ultrametric structure that emerges. Four or five subgroups of languages are identified, according to the "cut" of the dendrogram, drawn with an entropic criterion. The results and the method are discussed.
* 10 pages, 12 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge