Key Phrase Classification in Complex Assignments
Paper and Code
Mar 16, 2020
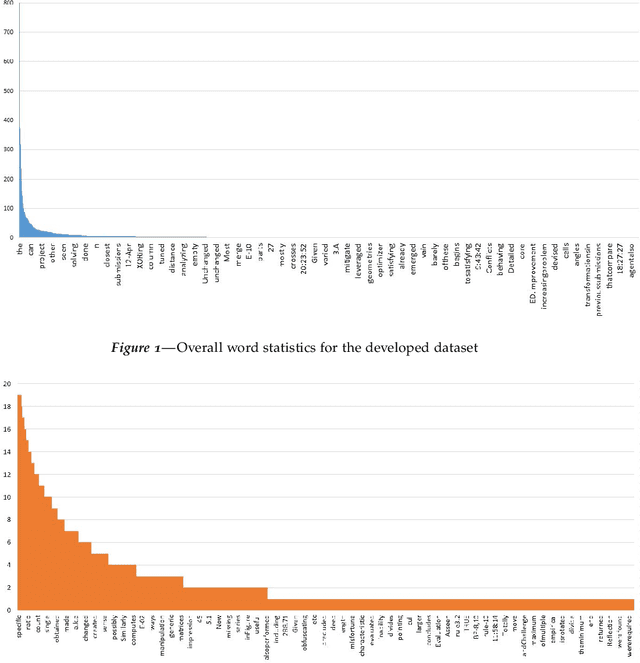
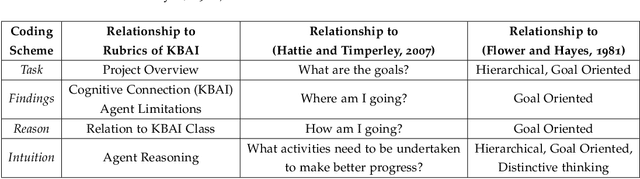
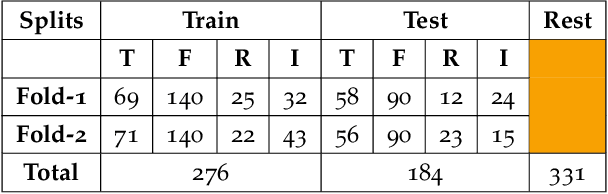
Complex assignments typically consist of open-ended questions with large and diverse content in the context of both classroom and online graduate programs. With the sheer scale of these programs comes a variety of problems in peer and expert feedback, including rogue reviews. As such with the hope of identifying important contents needed for the review, in this work we present a very first work on key phrase classification with a detailed empirical study on traditional and most recent language modeling approaches. From this study, we find that the task of classification of key phrases is ambiguous at a human level producing Cohen's kappa of 0.77 on a new data set. Both pretrained language models and simple TFIDF SVM classifiers produce similar results with a former producing average of 0.6 F1 higher than the latter. We finally derive practical advice from our extensive empirical and model interpretability results for those interested in key phrase classification from educational reports in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge