Joint Named Entity Recognition and Stance Detection in Tweets
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2017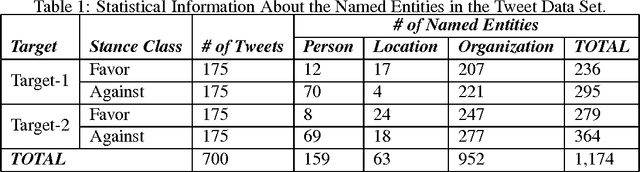
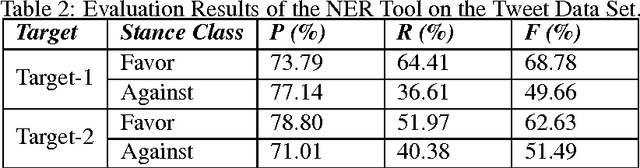
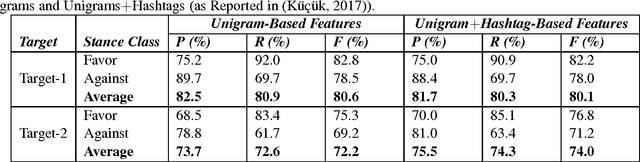
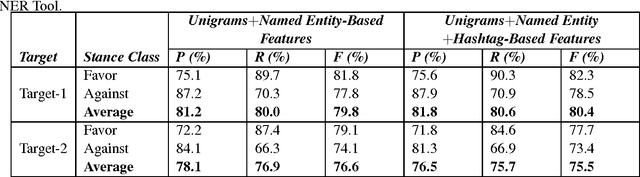
Named entity recognition (NER) is a well-established task of information extraction which has been studied for decades. More recently, studies reporting NER experiments on social media texts have emerged. On the other hand, stance detection is a considerably new research topic usually considered within the scope of sentiment analysis. Stance detection studies are mostly applied to texts of online debates where the stance of the text owner for a particular target, either explicitly or implicitly mentioned in text, is explored. In this study, we investigate the possible contribution of named entities to the stance detection task in tweets. We report the evaluation results of NER experiments as well as that of the subsequent stance detection experiments using named entities, on a publicly-available stance-annotated data set of tweets. Our results indicate that named entities obtained with a high-performance NER system can contribute to stance detection performance on tweets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge