Joint ML-Bayesian Approach to Adaptive Radar Detection in the presence of Gaussian Interference
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2025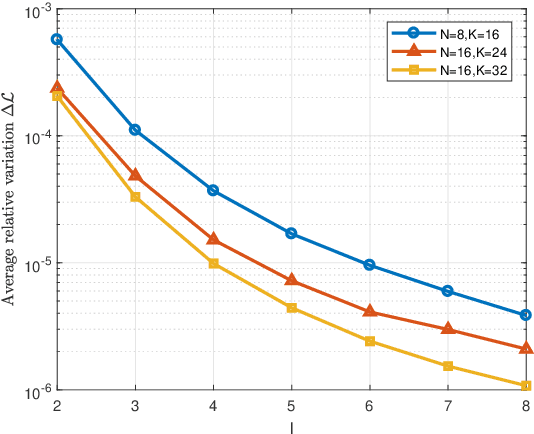
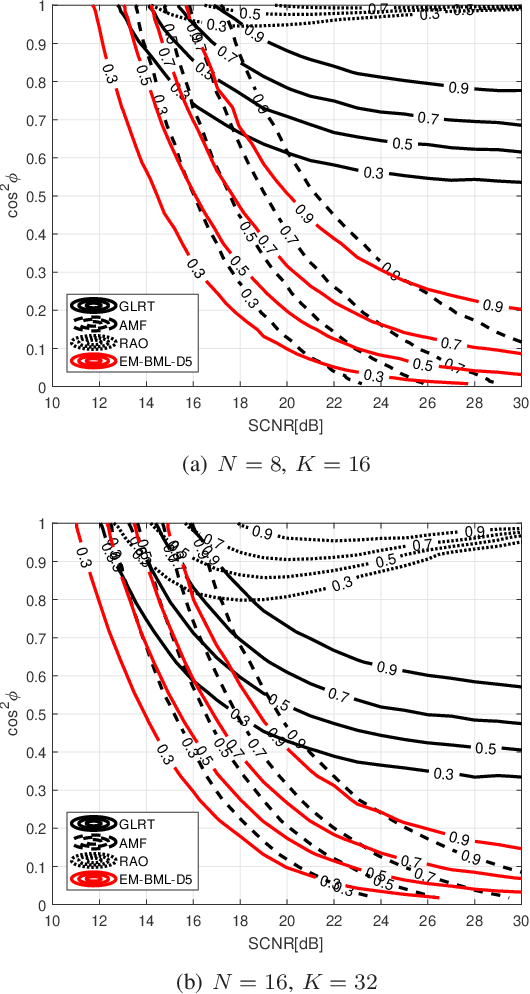
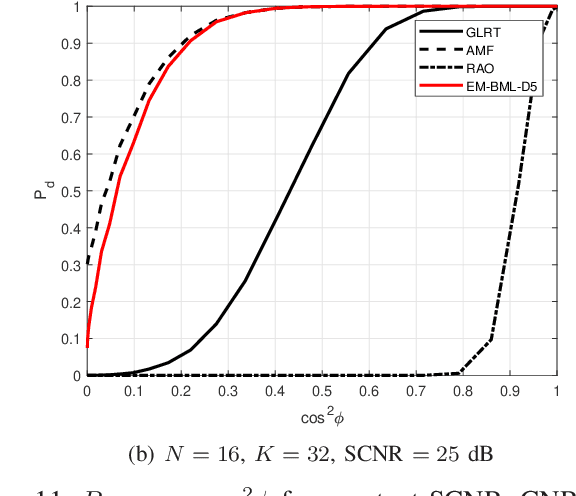
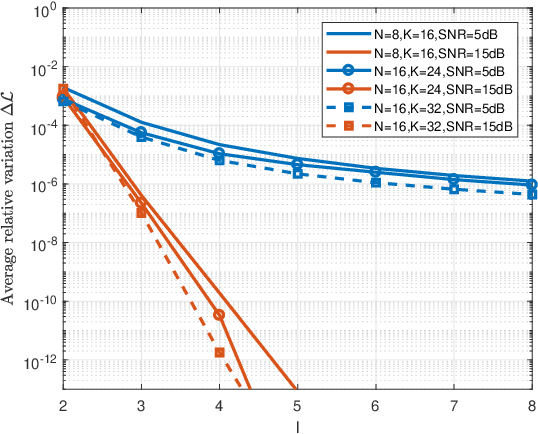
This paper addresses the adaptive radar target detection problem in the presence of Gaussian interference with unknown statistical properties. To this end, the problem is first formulated as a binary hypothesis test, and then we derive a detection architecture grounded on the hybrid of Maximum Likelihood (ML) and Maximum A Posterior (MAP) approach. Specifically, we resort to the hidden discrete latent variables in conjunction with the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithms which cyclically updates the estimates of the unknowns. In this framework, the estimates of the a posteriori probabilities under each hypothesis are representative of the inherent nature of data and used to decide for the presence of a potential target. In addition, we prove that the developed detection scheme ensures the desired Constant False Alarm Rate property with respect to the unknown interference covariance matrix. Numerical examples obtained through synthetic and real recorded data corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed architecture and show that the MAP-based approach ensures evident improvement with respect to the conventional generalized likelihood ratio test at least for the considered scenarios and parameter setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge