Joint Hybrid Transceiver and Reflection Matrix Design for RIS-Aided mmWave MIMO Cognitive Radio Systems
Paper and Code
Jun 13, 2024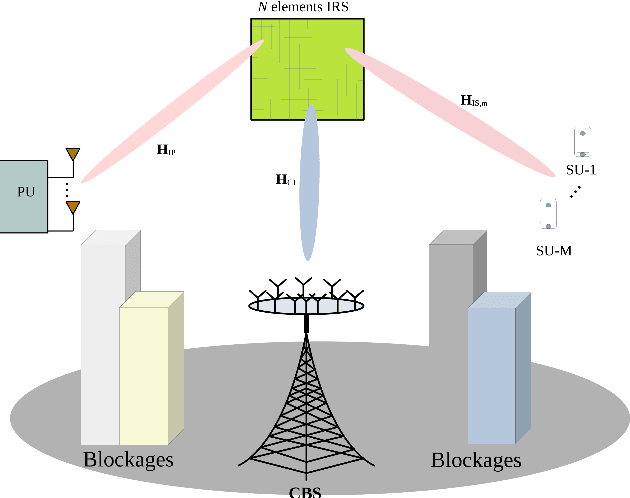
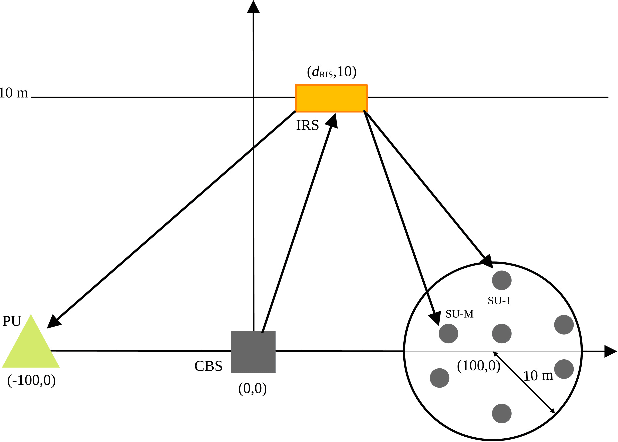
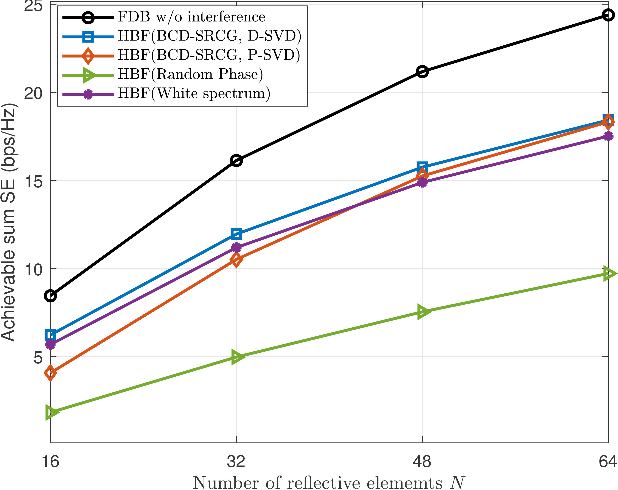
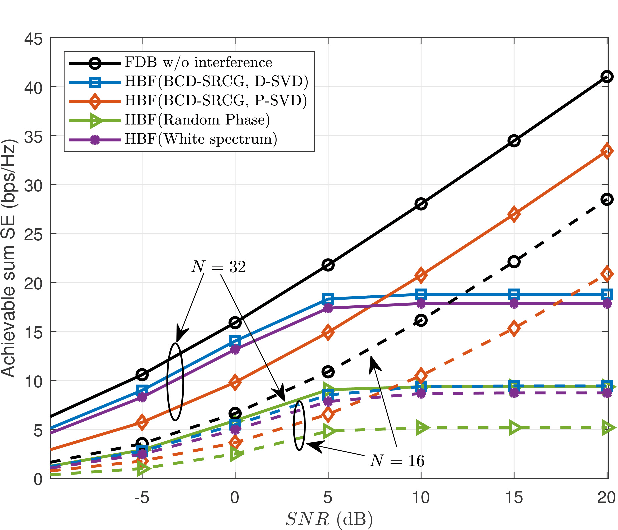
In this work, a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided millimeter wave (mmWave) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) cognitive radio (CR) downlink operating in the underlay mode is investigated. The cognitive base station (CBS) communicates with multiple secondary users (SUs), each having multiple RF chains in the presence of a primary user (PU). We conceive a joint hybrid transmit precoder (TPC), receiver combiner (RC), and RIS reflection matrix (RM) design, which maximizes the sum spectral efficiency (SE) of the secondary system while maintaining the interference induced at the PU below a specified threshold. To this end, we formulate the sum-SE maximization problem considering the total transmit power (TP), the interference power (IP), and the non-convex unity modulus constraints of the RF TPC, RF RC, and RM. To solve this highly non-convex problem, we propose a two-stage hybrid transceiver design in conjunction with a novel block coordinate descent (BCD)-successive Riemannian conjugate gradient (SRCG) algorithm. We initially decompose the RF TPC, RC, and RM optimization problem into a series of sub-problems and subsequently design pairs of RF TPC and RC vectors, followed by successively optimizing the elements of the RM using the iterative BCD-SRCG algorithm. Furthermore, based on the effective baseband (BB) channel, the BB TPC and BB RC are designed using the proposed direct singular value decomposition (D-SVD) and projection based SVD (P-SVD) methods. Subsequently, the proportional water-filling solution is proposed for optimizing the power, which maximizes the weighted sum-SE of the system. Finally, simulation results are provided to compare our proposed schemes to several benchmarks and quantify the impact of other parameters on the sum-SE of the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge