It is hard to see a needle in a haystack: Modeling contrast masking effect in a numerical observer
Paper and Code
Aug 05, 2014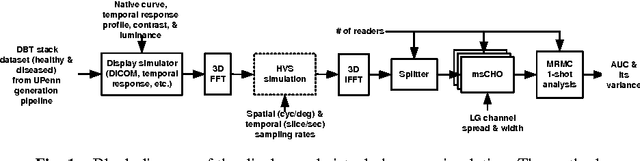
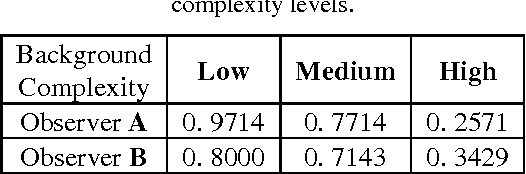
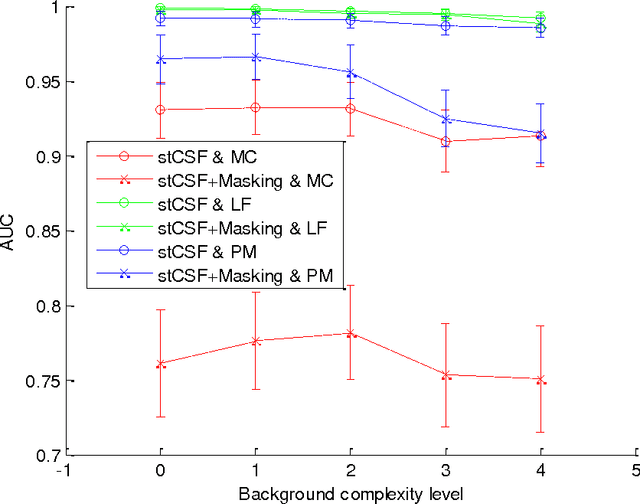
Within the framework of a virtual clinical trial for breast imaging, we aim to develop numerical observers that follow the same detection performance trends as those of a typical human observer. In our prior work, we showed that by including spatiotemporal contrast sensitivity function (stCSF) of human visual system (HVS) in a multi-slice channelized Hotelling observer (msCHO), we can correctly predict trends of a typical human observer performance with the viewing parameters of browsing speed, viewing distance and contrast. In this work we further improve our numerical observer by modeling contrast masking. After stCSF, contrast masking is the second most prominent property of HVS and it refers to the fact that the presence of one signal affects the visibility threshold for another signal. Our results indicate that the improved numerical observer better predicts changes in detection performance with background complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge