Is My Data in Your Retrieval Database? Membership Inference Attacks Against Retrieval Augmented Generation
Paper and Code
May 30, 2024


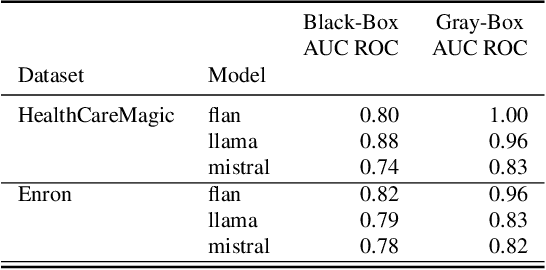
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have shown great promise in natural language processing. However, their reliance on data stored in a retrieval database, which may contain proprietary or sensitive information, introduces new privacy concerns. Specifically, an attacker may be able to infer whether a certain text passage appears in the retrieval database by observing the outputs of the RAG system, an attack known as a Membership Inference Attack (MIA). Despite the significance of this threat, MIAs against RAG systems have yet remained under-explored. This study addresses this gap by introducing an efficient and easy-to-use method for conducting MIA against RAG systems. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our attack using two benchmark datasets and multiple generative models, showing that the membership of a document in the retrieval database can be efficiently determined through the creation of an appropriate prompt in both black-box and gray-box settings. Our findings highlight the importance of implementing security countermeasures in deployed RAG systems to protect the privacy and security of retrieval databases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge