Is Gender "In-the-Wild" Inference Really a Solved Problem?
Paper and Code
May 12, 2021
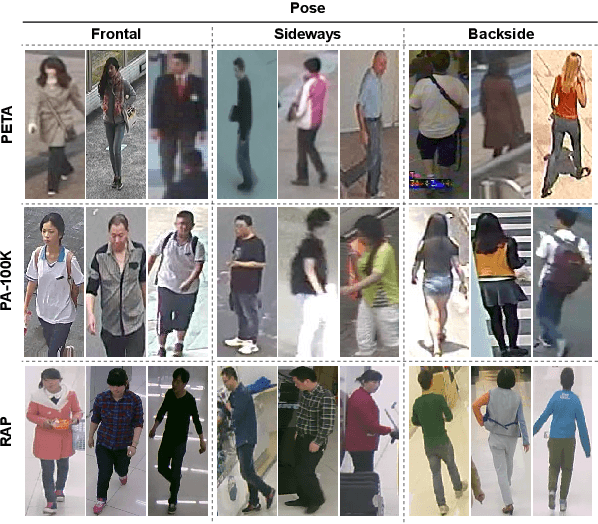
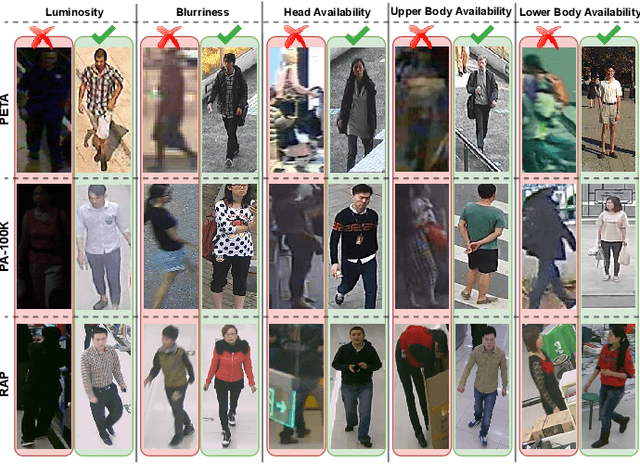


Soft biometrics analysis is seen as an important research topic, given its relevance to various applications. However, even though it is frequently seen as a solved task, it can still be very hard to perform in wild conditions, under varying image conditions, uncooperative poses, and occlusions. Considering the gender trait as our topic of study, we report an extensive analysis of the feasibility of its inference regarding image (resolution, luminosity, and blurriness) and subject-based features (face and body keypoints confidence). Using three state-of-the-art datasets (PETA, PA-100K, RAP) and five Person Attribute Recognition models, we correlate feature analysis with gender inference accuracy using the Shapley value, enabling us to perceive the importance of each image/subject-based feature. Furthermore, we analyze face-based gender inference and assess the pose effect on it. Our results suggest that: 1) image-based features are more influential for low-quality data; 2) an increase in image quality translates into higher subject-based feature importance; 3) face-based gender inference accuracy correlates with image quality increase; and 4) subjects' frontal pose promotes an implicit attention towards the face. The reported results are seen as a basis for subsequent developments of inference approaches in uncontrolled outdoor environments, which typically correspond to visual surveillance conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge