Is Einstein more agreeable and less neurotic than Hitler? A computational exploration of the emotional and personality profiles of historical persons
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2021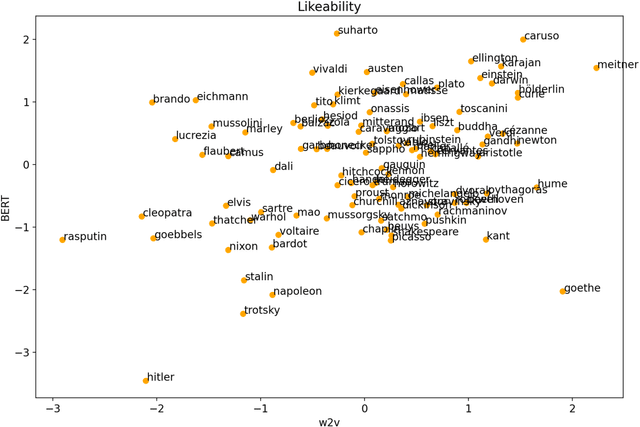
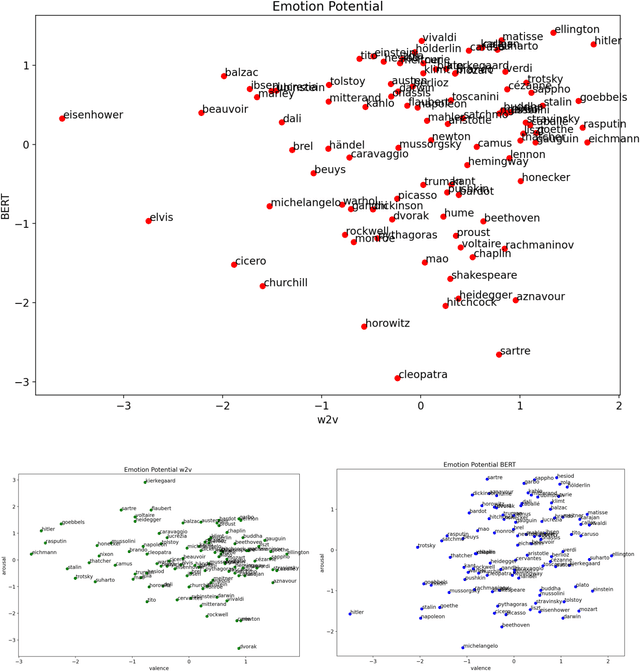
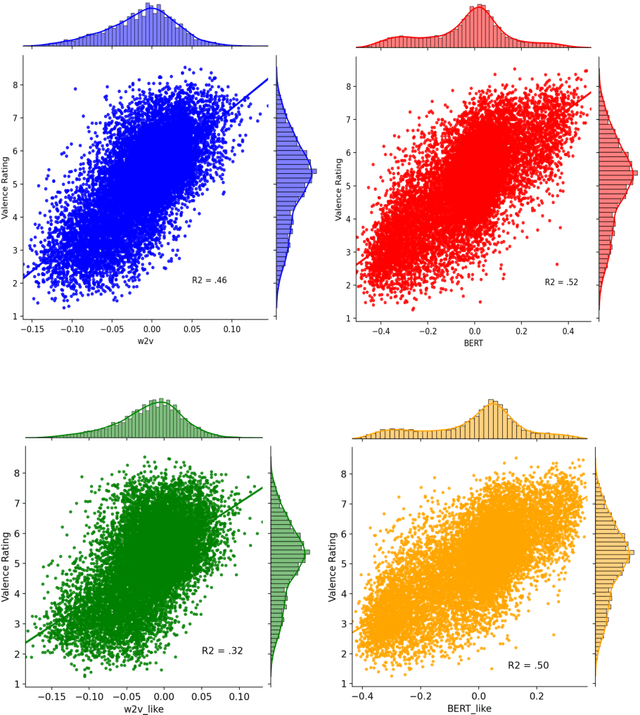
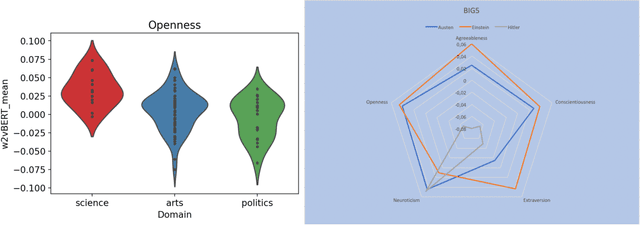
Recent progress in distributed semantic models (DSM) offers new ways to estimate personality traits of both fictive and real people. In this exploratory study we applied an extended version of the algorithm developed in Jacobs (2019) to compute the likeability scores, emotional figure profiles and BIG5 personality traits for 100 historical persons from the arts, politics or science domains whose names are rather unique (e.g., Einstein, Kahlo, Picasso). We compared the results produced by static (word2vec) and dynamic (BERT) language model representations in four studies. The results show both the potential and limitations of such DSM-based computations of personality profiles and point ways to further develop this approach to become a useful tool in data science, psychology or computational and neurocognitive poetics (Jacobs, 2015).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge