Interpretable Stochastic Block Influence Model: measuring social influence among homophilous communities
Paper and Code
Jun 01, 2020
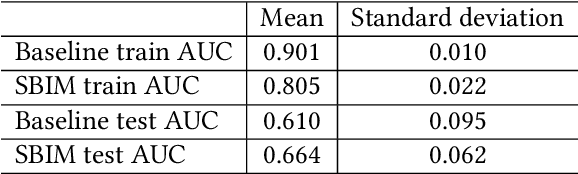
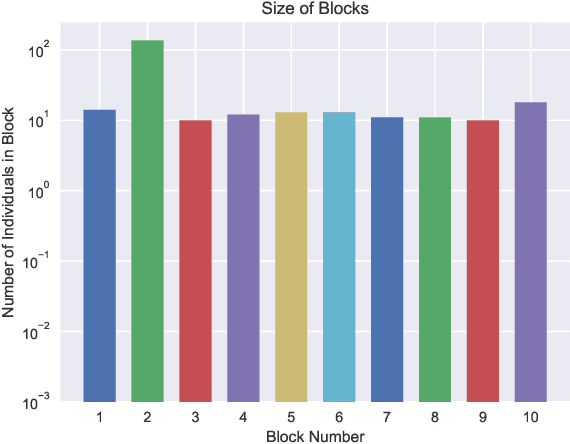

Decision-making on networks can be explained by both homophily and social influence. While homophily drives the formation of communities with similar characteristics, social influence occurs both within and between communities. Social influence can be reasoned through role theory, which indicates that the influences among individuals depend on their roles and the behavior of interest. To operationalize these social science theories, we empirically identify the homophilous communities and use the community structures to capture the "roles", which affect the particular decision-making processes. We propose a generative model named Stochastic Block Influence Model and jointly analyze both the network formation and the behavioral influence within and between different empirically-identified communities. To evaluate the performance and demonstrate the interpretability of our method, we study the adoption decisions of microfinance in an Indian village. We show that although individuals tend to form links within communities, there are strong positive and negative social influences between communities, supporting the weak tie theory. Moreover, we find that communities with shared characteristics are associated with positive influence. In contrast, the communities with a lack of overlap are associated with negative influence. Our framework facilitates the quantification of the influences underlying decision communities and is thus a useful tool for driving information diffusion, viral marketing, and technology adoptions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge