Interpretable Multi-task Learning with Shared Variable Embeddings
Paper and Code
May 10, 2024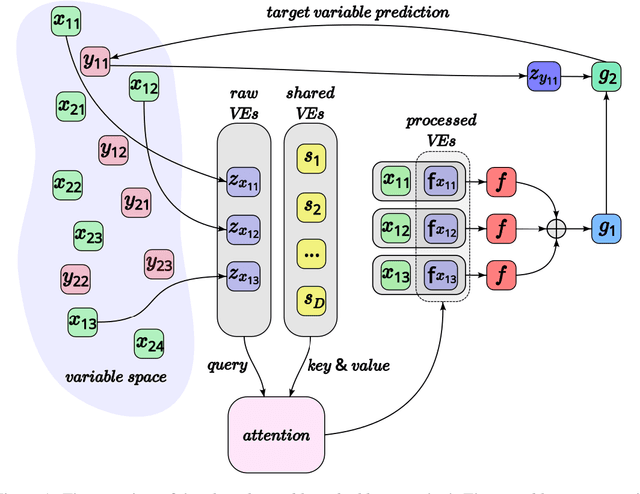
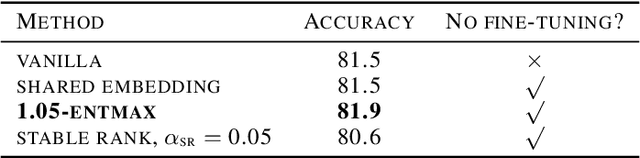
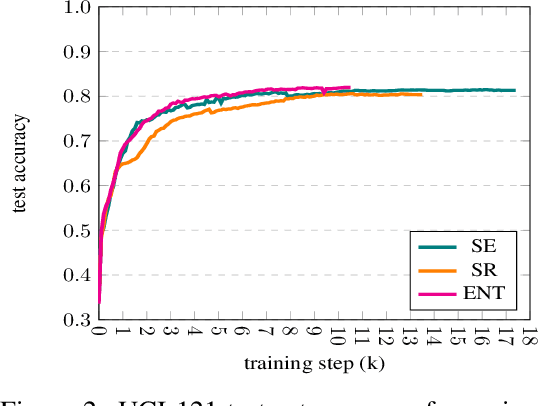
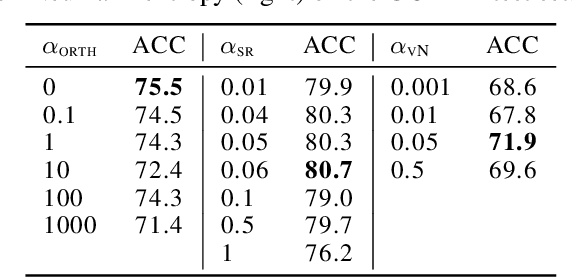
This paper proposes a general interpretable predictive system with shared information. The system is able to perform predictions in a multi-task setting where distinct tasks are not bound to have the same input/output structure. Embeddings of input and output variables in a common space are obtained, where the input embeddings are produced through attending to a set of shared embeddings, reused across tasks. All the embeddings are treated as model parameters and learned. Specific restrictions on the space of shared embedings and the sparsity of the attention mechanism are considered. Experiments show that the introduction of shared embeddings does not deteriorate the results obtained from a vanilla variable embeddings method. We run a number of further ablations. Inducing sparsity in the attention mechanism leads to both an increase in accuracy and a significant decrease in the number of training steps required. Shared embeddings provide a measure of interpretability in terms of both a qualitative assessment and the ability to map specific shared embeddings to pre-defined concepts that are not tailored to the considered model. There seems to be a trade-off between accuracy and interpretability. The basic shared embeddings method favors interpretability, whereas the sparse attention method promotes accuracy. The results lead to the conclusion that variable embedding methods may be extended with shared information to provide increased interpretability and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge