Interpretable Automated Diagnosis of Retinal Disease using Deep OCT Analysis
Paper and Code
Sep 03, 2021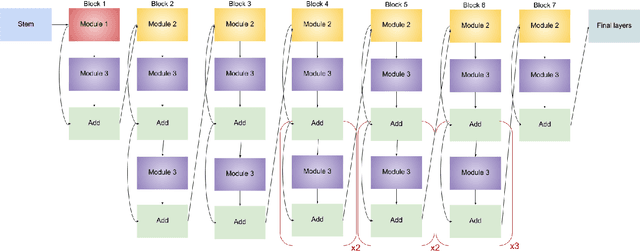
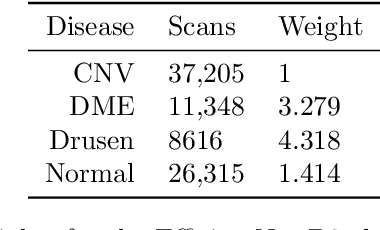

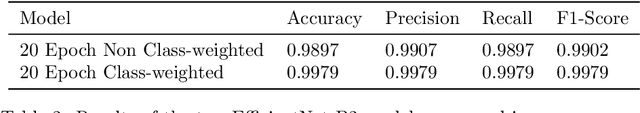
30 million Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) imaging tests are issued every year to diagnose various retinal diseases, but accurate diagnosis of OCT scans requires trained ophthalmologists who are still prone to making misclassifications. With better systems for diagnosis, many cases of vision loss caused by retinal disease could be entirely avoided. In this work, we developed a CNN-based model for accurate classification of CNV, DME, Drusen, and Normal OCT scans. Furthermore, we placed an emphasis on producing both qualitative and quantitative explanations of the model's decisions. Our class-weighted EfficientNet B2 classification model performed at 99.79% accuracy. We then produced and analyzed heatmaps of where in the OCT scan the model focused. After producing the heatmaps, we created breakdowns of the specific retinal layers the model focused on. While highly accurate models have been previously developed, our work is the first to produce detailed explanations of the model's decisions. The combination of accuracy and interpretability in our work can be clinically applied for better patient care. Future work can use a similar model for classification on larger and more diverse data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge