Interpretable and Generalizable Graph Learning via Stochastic Attention Mechanism
Paper and Code
Jan 31, 2022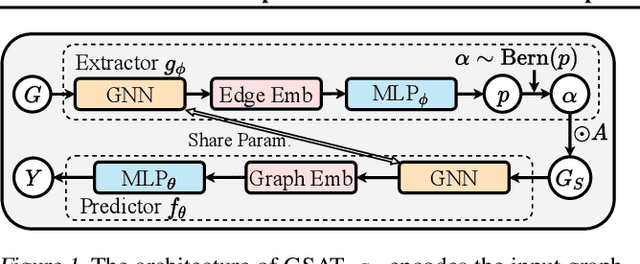
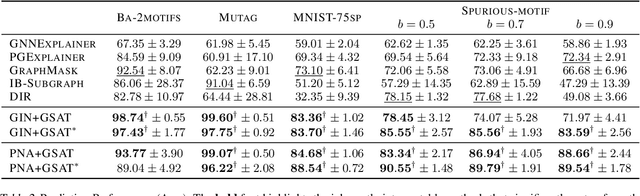

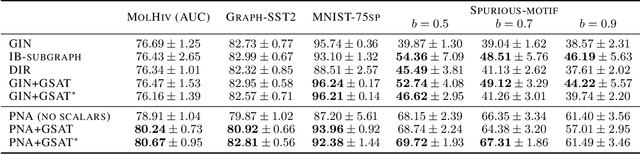
Interpretable graph learning is in need as many scientific applications depend on learning models to collect insights from graph-structured data. Previous works mostly focused on using post-hoc approaches to interpret a pre-trained model (graph neural network models in particular). They argue against inherently interpretable models because good interpretation of these models is often at the cost of their prediction accuracy. And, the widely used attention mechanism for inherent interpretation often fails to provide faithful interpretation in graph learning tasks. In this work, we address both issues by proposing Graph Stochastic Attention (GSAT), an attention mechanism derived from the information bottleneck principle. GSAT leverages stochastic attention to block the information from the task-irrelevant graph components while learning stochasticity-reduced attention to select the task-relevant subgraphs for interpretation. GSAT can also apply to fine-tuning and interpreting pre-trained models via stochastic attention mechanism. Extensive experiments on eight datasets show that GSAT outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by up to 20%$\uparrow$ in interpretation AUC and 5%$\uparrow$ in prediction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge