Interference Cancellation Algorithms for Grant-Free Multiple Access with Massive MIMO
Paper and Code
May 15, 2023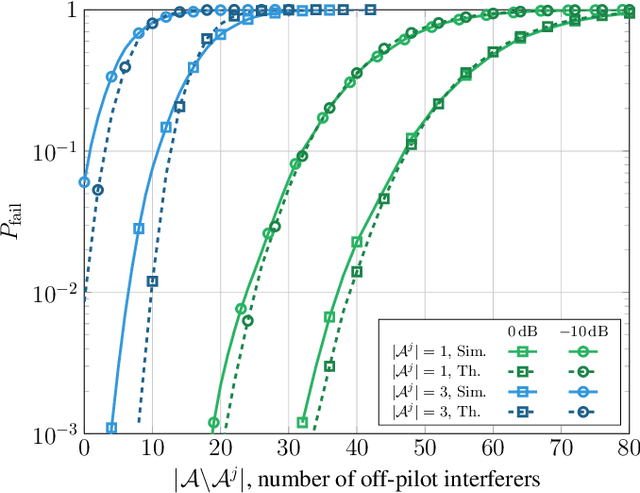
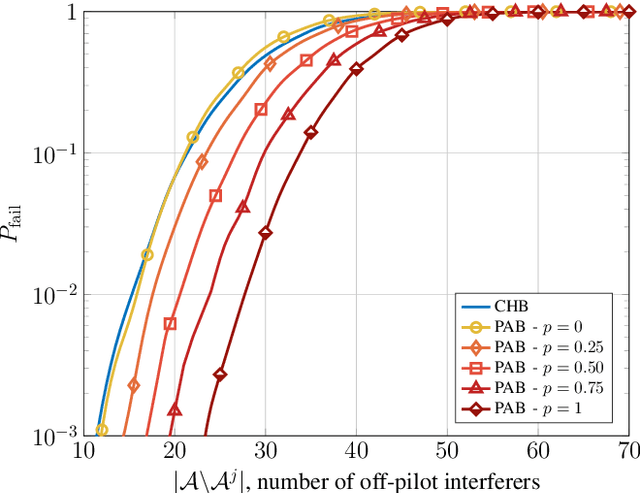
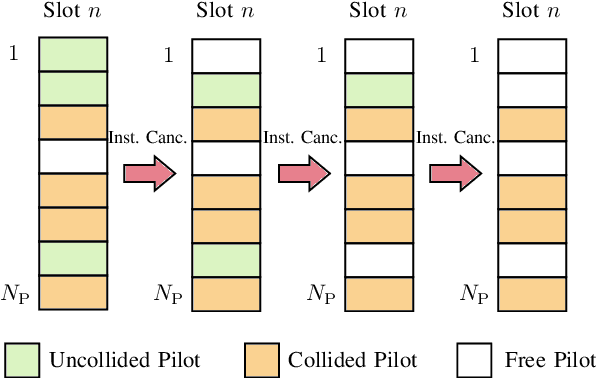
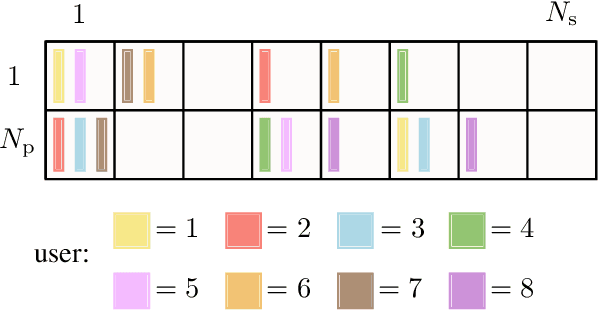
In next generation Internet-of-Things, the overhead introduced by grant-based multiple access protocols may engulf the access network as a consequence of the unprecedented number of connected devices. Grant-free access protocols are therefore gaining an increasing interest to support massive access from machine-type devices with intermittent activity. In this paper, coded random access (CRA) with massive multiple input multiple output (MIMO) is investigated as a solution to design highly-scalable massive multiple access protocols, taking into account stringent requirements on latency and reliability. With a focus on signal processing aspects at the physical layer and their impact on the overall system performance, critical issues of successive interference cancellation (SIC) over fading channels are first analyzed. Then, SIC algorithms and a scheduler are proposed that can overcome some of the limitations of the current access protocols. The effectiveness of the proposed processing algorithms is validated by Monte Carlo simulation, for different CRA protocols and by comparisons with developed benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge