Integrating Multiple Receptive Fields through Grouped Active Convolution
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2018


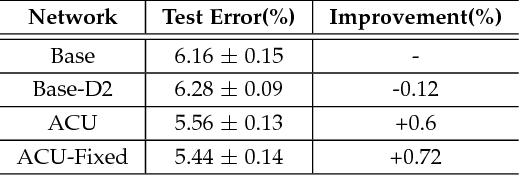
Convolutional networks have achieved great success in various vision tasks. This is mainly due to a considerable amount of research on network structure. In this study, instead of focusing on architectures, we focused on the convolution unit itself. The existing convolution unit has a fixed shape, and is limited to observing restricted receptive fields. In an earlier work, we proposed the active convolution unit (ACU), which can freely define its shape and learn by itself. In this paper, we propose a detailed analysis of the proposed unit and show that it is an efficient representation of a sparse weight convolution. Furthermore, we expand the unit to a grouped ACU, which can observe multiple receptive fields in one layer. We found that the performance of a naive grouped convolution is degraded by increasing the number of groups; however, the proposed unit retains the accuracy even though the number of parameters reduces. Based on this result, we suggest a depthwise ACU, and various experiments have shown that our unit is efficient and can replace the existing convolutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge