Information Planning for Text Data
Paper and Code
Mar 21, 2018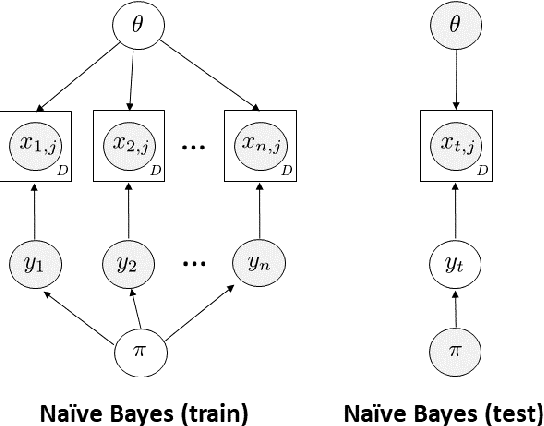


Information planning enables faster learning with fewer training examples. It is particularly applicable when training examples are costly to obtain. This work examines the advantages of information planning for text data by focusing on three supervised models: Naive Bayes, supervised LDA and deep neural networks. We show that planning based on entropy and mutual information outperforms random selection baseline and therefore accelerates learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge