Influence of Image Classification Accuracy on Saliency Map Estimation
Paper and Code
Jul 27, 2018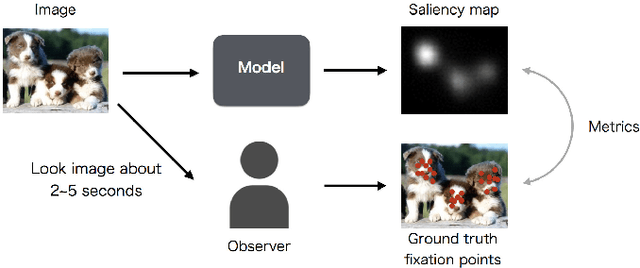



Saliency map estimation in computer vision aims to estimate the locations where people gaze in images. Since people tend to look at objects in images, the parameters of the model pretrained on ImageNet for image classification are useful for the saliency map estimation. However, there is no research on the relationship between the image classification accuracy and the performance of the saliency map estimation. In this paper, it is shown that there is a strong correlation between image classification accuracy and saliency map estimation accuracy. We also investigated the effective architecture based on multi scale images and the upsampling layers to refine the saliency-map resolution. Our model achieved the state-of-the-art accuracy on the PASCAL-S, OSIE, and MIT1003 datasets. In the MIT Saliency Benchmark, our model achieved the best performance in some metrics and competitive results in the other metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge