Improving Vertical Positioning Accuracy with the Weighted Multinomial Logistic Regression Classifier
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2020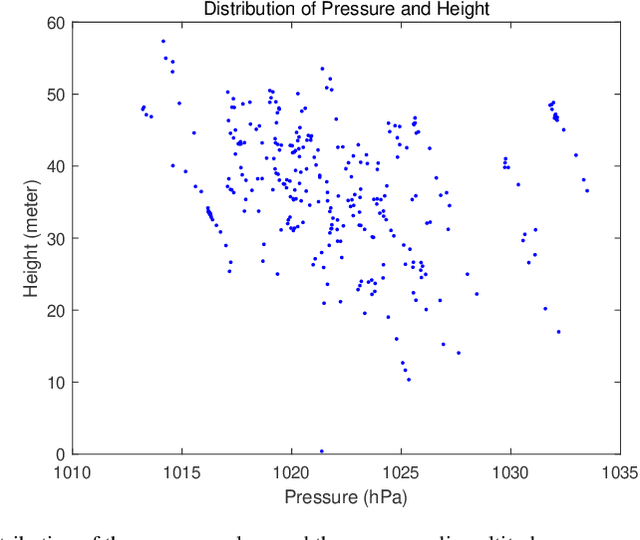
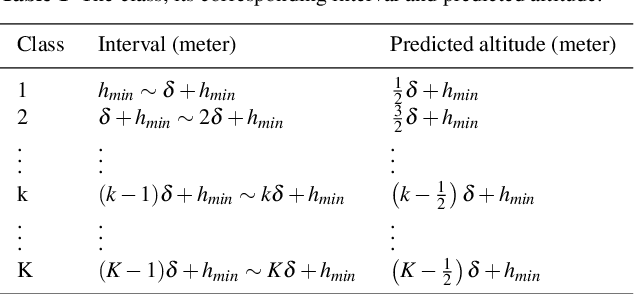
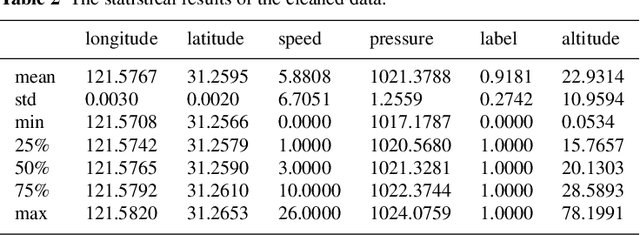
In this paper, a method of improving vertical positioning accuracy with the Global Positioning System (GPS) information and barometric pressure values is proposed. Firstly, we clear null values for the raw data collected in various environments, and use the 3$\sigma$-rule to identify outliers. Secondly, the Weighted Multinomial Logistic Regression (WMLR) classifier is trained to obtain the predicted altitude of outliers. Finally, in order to verify its effect, we compare the MLR method, the WMLR method, and the Support Vector Machine (SVM) method for the cleaned dataset which is regarded as the test baseline. The numerical results show that the vertical positioning accuracy is improved from 5.9 meters (the MLR method), 5.4 meters (the SVM method) to 5 meters (the WMLR method) for 67% test points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge