Improving Place Recognition Using Dynamic Object Detection
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2020
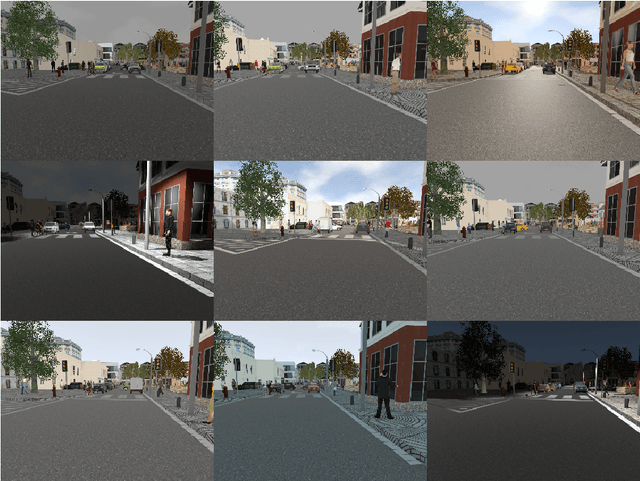
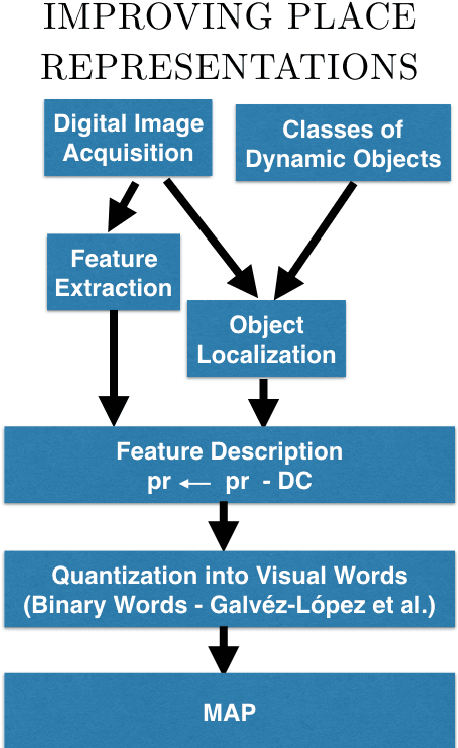
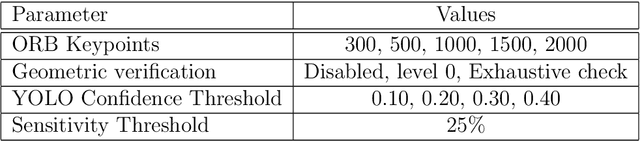

Traditional appearance-based place recognition algorithms based on handcrafted features have proven inadequate in environments with a significant presence of dynamic objects -- objects that may or may not be present in an agent's subsequent visits. Place representations from features extracted using Deep Learning approaches have gained popularity for their robustness and because the algorithms that used them yield better accuracy. Nevertheless, handcrafted features are still popular in devices that have limited resources. This article presents a novel approach that improves place recognition in environments populated by dynamic objects by incorporating the very knowledge of these objects to improve the overall quality of the representations of places used for matching. The proposed approach fuses object detection and place description, Deep Learning and handcrafted features, with the significance of reducing memory and storage requirements. This article demonstrates that the proposed approach yields improved place recognition accuracy, and was evaluated using both synthetic and real-world datasets. The adoption of the proposed approach will significantly improve place recognition results in environments populated by dynamic objects, and explored by devices with limited resources, with particular utility in both indoor and outdoor environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge