Improved selective background Monte Carlo simulation at Belle II with graph attention networks and weighted events
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2023


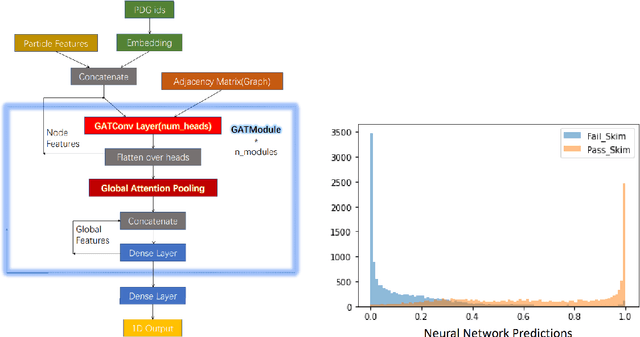
When measuring rare processes at Belle II, a huge luminosity is required, which means a large number of simulations are necessary to determine signal efficiencies and background contributions. However, this process demands high computation costs while most of the simulated data, in particular in case of background, are discarded by the event selection. Thus, filters using graph neural networks are introduced at an early stage to save the resources for the detector simulation and reconstruction of events discarded at analysis level. In our work, we improved the performance of the filters using graph attention and investigated statistical methods including sampling and reweighting to deal with the biases introduced by the filtering.
* to be published in ACAT 2022 proceedings in the Journal Of Physics:
Conference Series
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge