Impact of Power Supply Noise on Image Sensor Performance in Automotive Applications
Paper and Code
Nov 24, 2020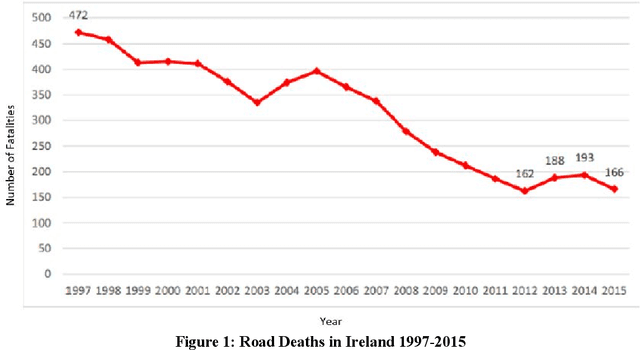
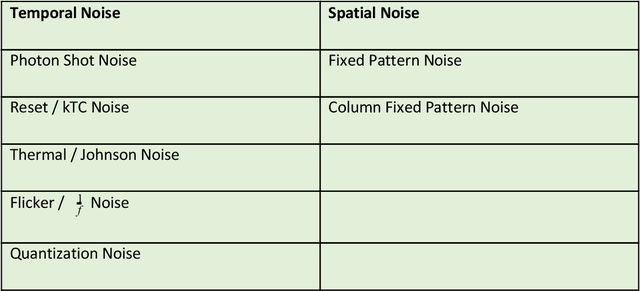
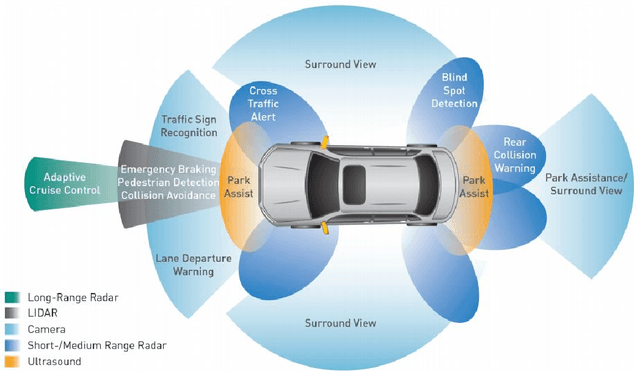
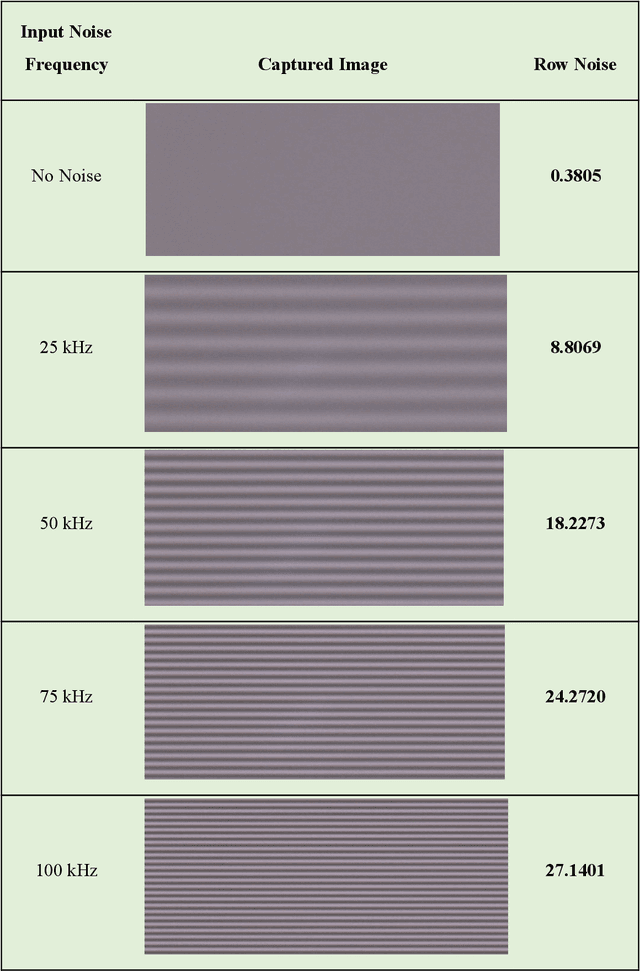
Vision Systems are quickly becoming a large component of Active Automotive Safety Systems. In order to be effective in critical safety applications these systems must produce high quality images in both daytime and night-time scenarios in order to provide the large informational content required for software analysis in applications such as lane departure, pedestrian detection and collision detection. The challenge in capturing high quality images in low light scenarios is that the signal to noise ratio is greatly reduced, which can result in noise becoming the dominant factor in a captured image, thereby making these safety systems less effective at night. Research has been undertaken to develop a systematic method of characterising image sensor performance in response to electrical noise in order to improve the design and performance of automotive cameras in low light scenarios. The root cause of image row noise has been established and a mathematical algorithm for determining the magnitude of row noise in an image has been devised. An automated characterisation method has been developed to allow performance characterisation in response to a large frequency spectrum of electrical noise on the image sensor power supply. Various strategies of improving image sensor performance for low light applications have also been proposed from the research outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge