Impact of Multiple Fully-Absorbing Receivers in Molecular Communications
Paper and Code
May 21, 2022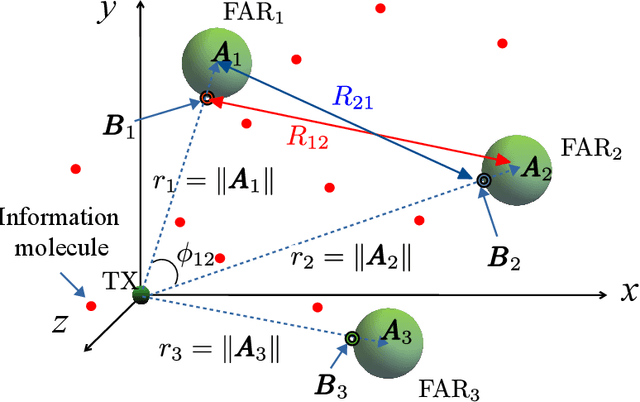
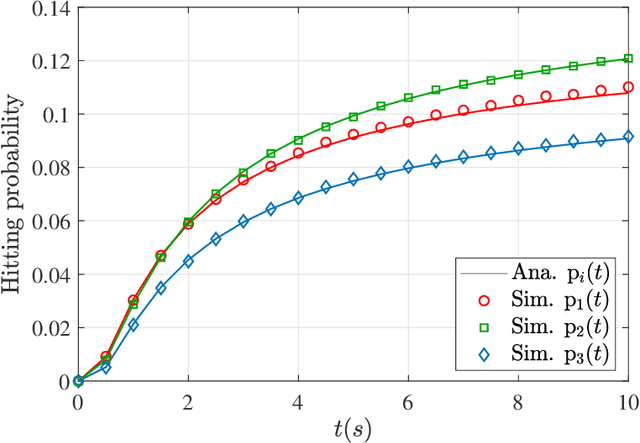
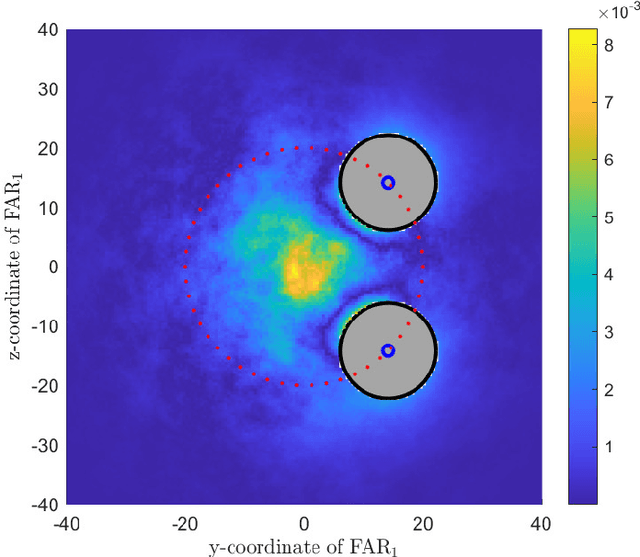
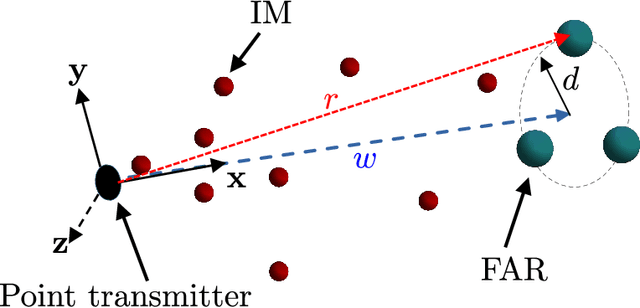
Molecular communication is a promising solution to enable intra-body communications among nanomachines. However, malicious and non-cooperative receivers can degrade the performance, compromising these systems' security. Analyzing the communication and security performance of these systems requires accurate channel models. However, such models are not present in the literature. In this work, we develop an analytical framework to derive the hitting probability of a molecule on a fully absorbing receiver (FAR) in the presence of other FARs, which can be either be cooperative or malicious. We first present an approximate hitting probability expression for the 3-FARs case. A simplified expression is obtained for the case when FARs are symmetrically positioned. Using the derived expressions, we study the impact of malicious receivers on the intended receiver and discuss how to minimize this impact to obtain a secure communication channel. We also study the gain that can be obtained by the cooperation of these FARs. We then present an approach to extend the analysis for a system with N FARs. The derived expressions can be used to analyze and design multiple input/output and secure molecular communication systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge