Impact of Explanation on Trust of a Novel Mobile Robot
Paper and Code
Jan 26, 2021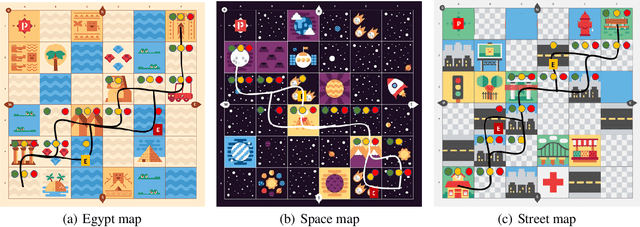
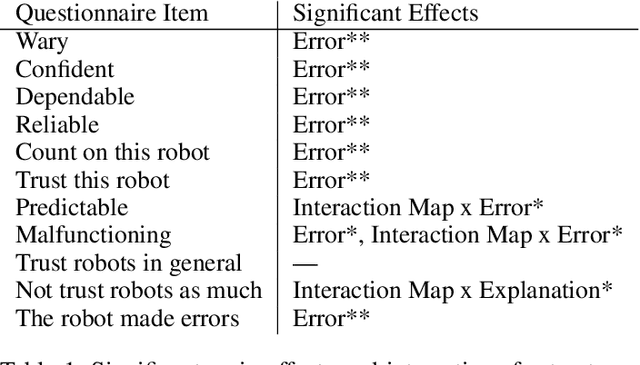
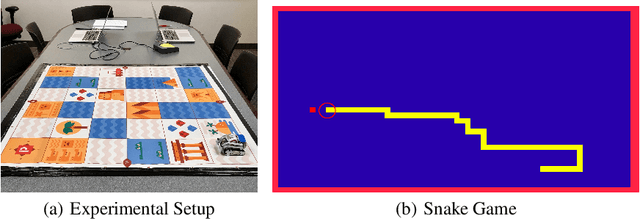
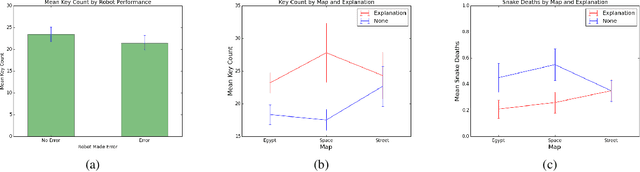
One challenge with introducing robots into novel environments is misalignment between supervisor expectations and reality, which can greatly affect a user's trust and continued use of the robot. We performed an experiment to test whether the presence of an explanation of expected robot behavior affected a supervisor's trust in an autonomous robot. We measured trust both subjectively through surveys and objectively through a dual-task experiment design to capture supervisors' neglect tolerance (i.e., their willingness to perform their own task while the robot is acting autonomously). Our objective results show that explanations can help counteract the novelty effect of seeing a new robot perform in an unknown environment. Participants who received an explanation of the robot's behavior were more likely to focus on their own task at the risk of neglecting their robot supervision task during the first trials of the robot's behavior compared to those who did not receive an explanation. However, this effect diminished after seeing multiple trials, and participants who received explanations were equally trusting of the robot's behavior as those who did not receive explanations. Interestingly, participants were not able to identify their own changes in trust through their survey responses, demonstrating that the dual-task design measured subtler changes in a supervisor's trust.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge