Hyperdimensional Computing for Efficient Distributed Classification with Randomized Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 02, 2021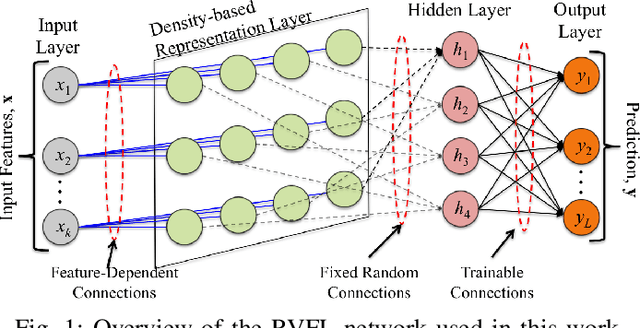
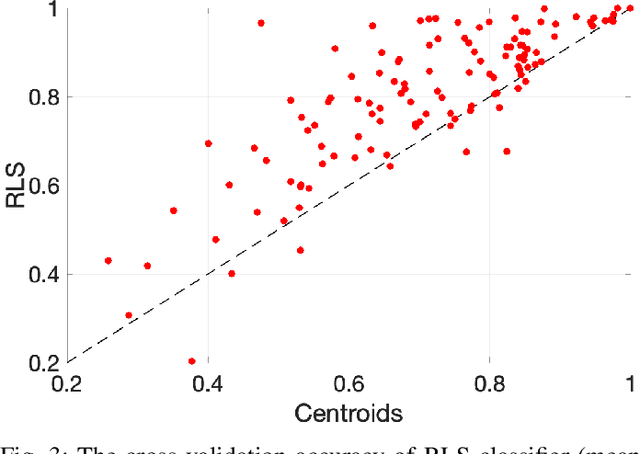
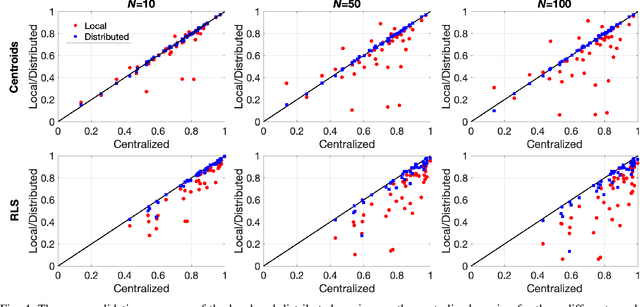
In the supervised learning domain, considering the recent prevalence of algorithms with high computational cost, the attention is steering towards simpler, lighter, and less computationally extensive training and inference approaches. In particular, randomized algorithms are currently having a resurgence, given their generalized elementary approach. By using randomized neural networks, we study distributed classification, which can be employed in situations were data cannot be stored at a central location nor shared. We propose a more efficient solution for distributed classification by making use of a lossy compression approach applied when sharing the local classifiers with other agents. This approach originates from the framework of hyperdimensional computing, and is adapted herein. The results of experiments on a collection of datasets demonstrate that the proposed approach has usually higher accuracy than local classifiers and getting close to the benchmark - the centralized classifier. This work can be considered as the first step towards analyzing the variegated horizon of distributed randomized neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge