House Markets and Single-Peaked Preferences: From Centralized to Decentralized Allocation Procedures
Paper and Code
Jun 24, 2019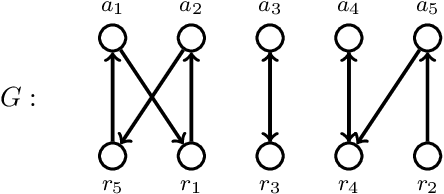
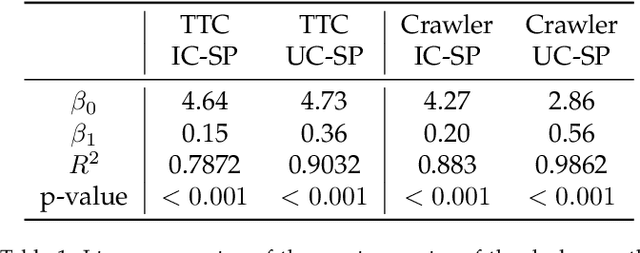
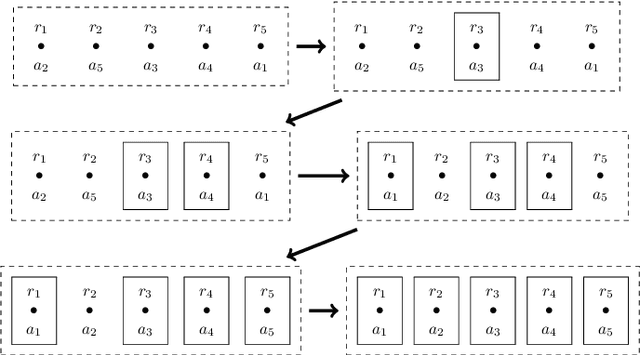
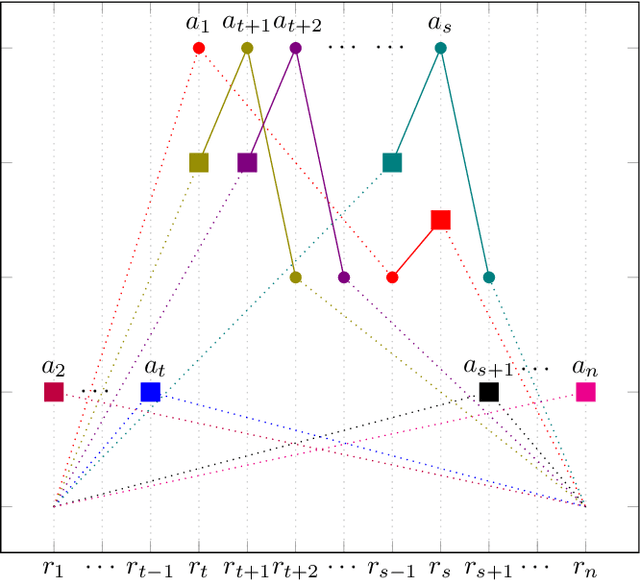
Recently, the problem of allocating one resource per agent with initial endowments (\emph{house markets}) has seen a renewed interest: indeed, while in the general domain Top Trading Cycle is known to be the only procedure guaranteeing Pareto-optimality, individual rationality, and strategy proofness, the situation differs in single-peaked domains. Bade (2019) presented the Crawler, an alternative procedure enjoying the same properties (with the additional advantage of being implementable in obviously dominant strategies); while Damamme et al. (2015) showed that allowing mutually beneficial swap-deals among the agents was already enough to guarantee Pareto-optimality. In this paper we significantly deepen our understanding of this decentralized procedures: we show in particular that the single-peaked domains happen to be ``maximal'' if one wishes to guarantee this convergence property. Interestingly, we also observe that the set of allocations reachable by swap-deals always contains the outcome of the Crawler. To further investigate how these different mechanisms compare, we pay special attention to the average and minimum rank of the resource obtained by the agents in the outcome allocation. We provide theoretical bounds on the loss potentially induced by these procedures with respect to these criteria, and complement these results with an extensive experimental study which shows how different variants of swap dynamics behave. In fact, even the simplest dynamics exhibit very good results, and it is possible to further guide the process towards our objectives, if one is ready to sacrifice a bit in terms of decentralization. On our way, we also show that a simple variant of the Crawler allows to check efficiently that an allocation is Pareto-optimal in single-peaked domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge