Holographic single particle imaging for weakly scattering, heterogeneous nanoscale objects
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2022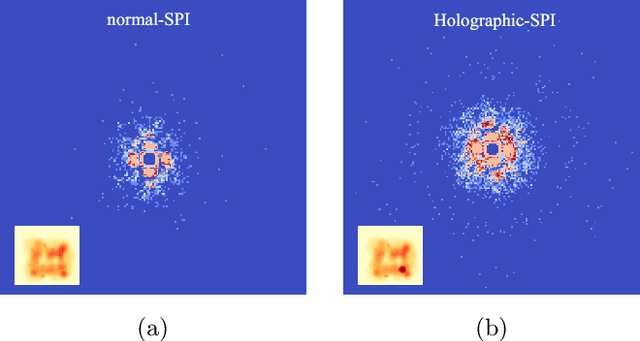
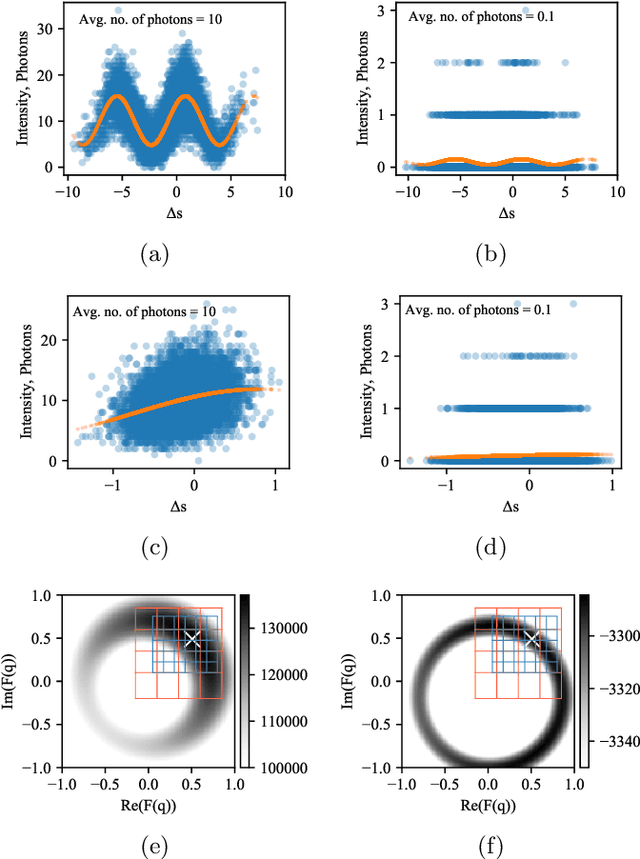
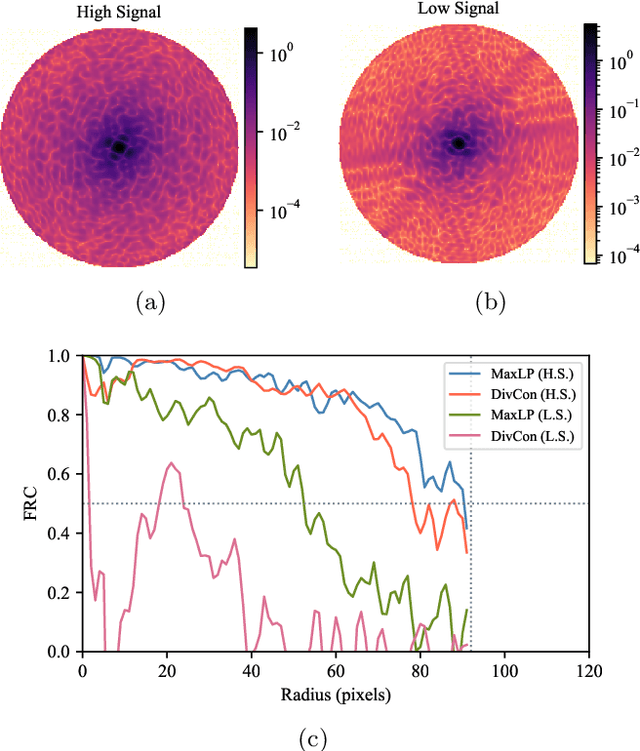
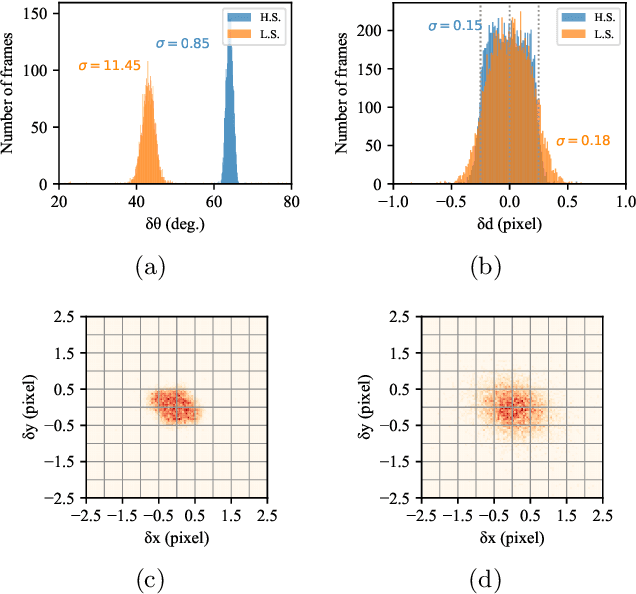
Single particle imaging (SPI) at X-ray free electron lasers (XFELs) is a technique to determine the 3D structure of nanoscale objects like biomolecules from a large number of diffraction patterns of copies of these objects in random orientations. Millions of low signal-to-noise diffraction patterns with unknown orientation are collected during an X-ray SPI experiment. The patterns are then analyzed and merged using a reconstruction algorithm to retrieve the full 3D-structure of particle. The resolution of reconstruction is limited by background noise, signal-to-noise ratio in diffraction patterns and total amount of data collected. We recently introduced a reference-enhanced holographic single particle imaging methodology [Optica 7,593-601(2020)] to collect high enough signal-to-noise and background tolerant patterns and a reconstruction algorithm to recover missing parameters beyond orientation and then directly retrieve the full Fourier model of the sample of interest. Here we describe a phase retrieval algorithm based on maximum likelihood estimation using pattern search dubbed as MaxLP, with better scalability for fine sampling of latent parameters and much better performance in the low signal limit. Furthermore, we show that structural variations within the target particle are averaged in real space, significantly improving robustness to conformational heterogeneity in comparison to conventional SPI. With these computational improvements, we believe reference-enhanced SPI is capable of reaching sub-nm resolution biomolecule imaging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge