HinDom: A Robust Malicious Domain Detection System based on Heterogeneous Information Network with Transductive Classification
Paper and Code
Sep 04, 2019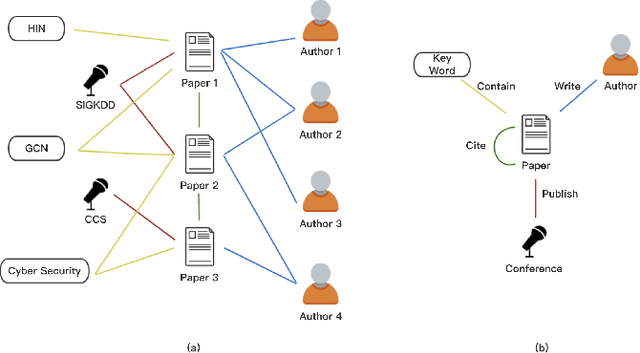
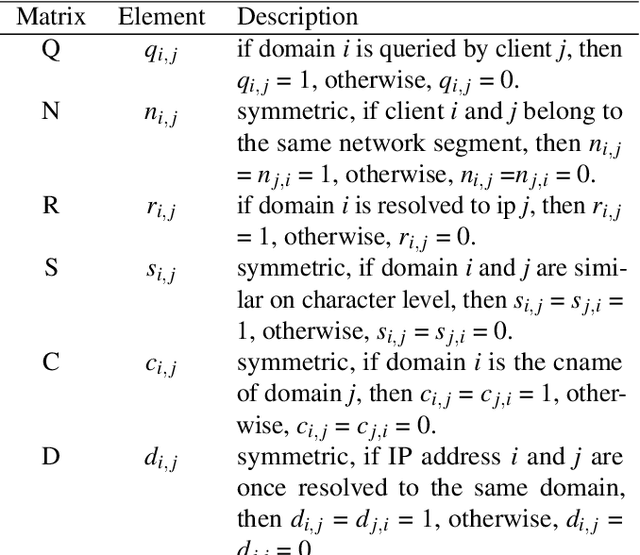
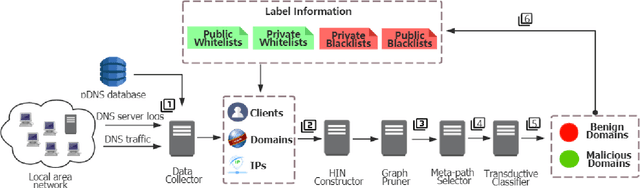
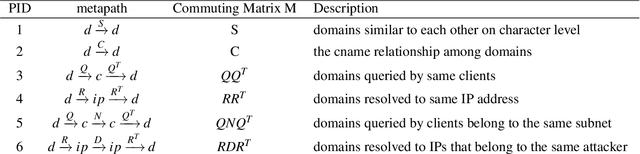
Domain name system (DNS) is a crucial part of the Internet, yet has been widely exploited by cyber attackers. Apart from making static methods like blacklists or sinkholes infeasible, some weasel attackers can even bypass detection systems with machine learning based classifiers. As a solution to this problem, we propose a robust domain detection system named HinDom. Instead of relying on manually selected features, HinDom models the DNS scene as a Heterogeneous Information Network (HIN) consist of clients, domains, IP addresses and their diverse relationships. Besides, the metapath-based transductive classification method enables HinDom to detect malicious domains with only a small fraction of labeled samples. So far as we know, this is the first work to apply HIN in DNS analysis. We build a prototype of HinDom and evaluate it in CERNET2 and TUNET. The results reveal that HinDom is accurate, robust and can identify previously unknown malicious domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge