HELLINGER-UCB: A novel algorithm for stochastic multi-armed bandit problem and cold start problem in recommender system
Paper and Code
Apr 16, 2024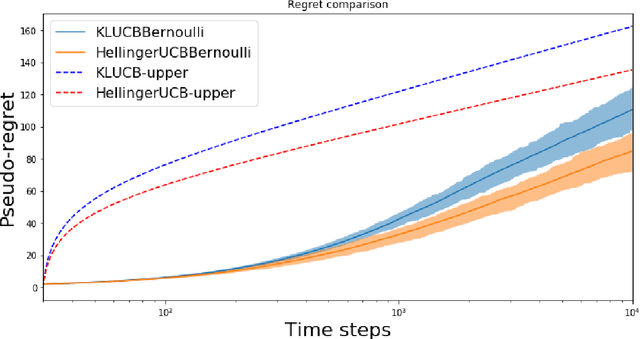

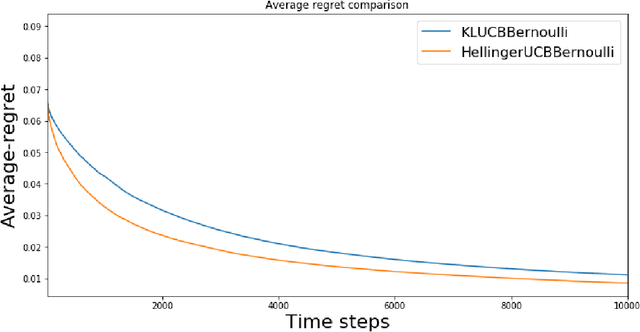
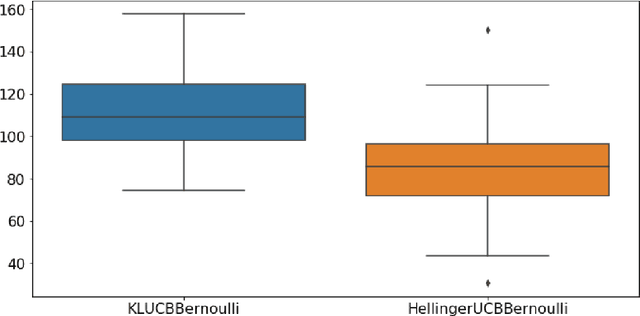
In this paper, we study the stochastic multi-armed bandit problem, where the reward is driven by an unknown random variable. We propose a new variant of the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) algorithm called Hellinger-UCB, which leverages the squared Hellinger distance to build the upper confidence bound. We prove that the Hellinger-UCB reaches the theoretical lower bound. We also show that the Hellinger-UCB has a solid statistical interpretation. We show that Hellinger-UCB is effective in finite time horizons with numerical experiments between Hellinger-UCB and other variants of the UCB algorithm. As a real-world example, we apply the Hellinger-UCB algorithm to solve the cold-start problem for a content recommender system of a financial app. With reasonable assumption, the Hellinger-UCB algorithm has a convenient but important lower latency feature. The online experiment also illustrates that the Hellinger-UCB outperforms both KL-UCB and UCB1 in the sense of a higher click-through rate (CTR).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge