Group-Representative Functional Network Estimation from Multi-Subject fMRI Data via MRF-based Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2018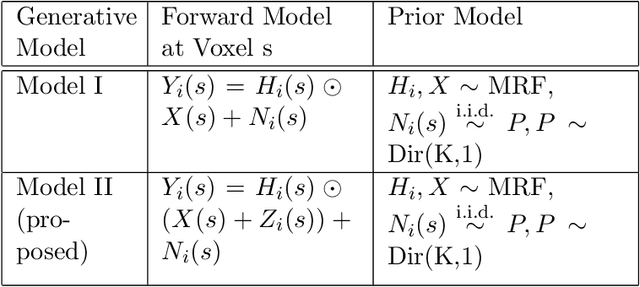


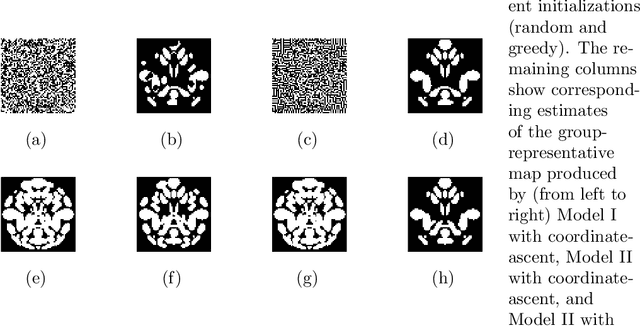
We propose a novel two-phase approach to functional network estimation of multi-subject functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) data, which applies model-based image segmentation to determine a group-representative connectivity map. In our approach, we first improve clustering-based Independent Component Analysis (ICA) to generate maps of components occurring consistently across subjects, and then estimate the group-representative map through MAP-MRF (Maximum a priori - Markov random field) labeling. For the latter, we provide a novel and efficient variational Bayes algorithm. We study the performance of the proposed method using synthesized data following a theoretical model, and demonstrate its viability in blind extraction of group-representative functional networks using simulated fMRI data. We anticipate the proposed method will be applied in identifying common neuronal characteristics in a population, and could be further extended to real-world clinical diagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge