Graph-based compensated wavelet lifting for 3-D+t medical CT data
Paper and Code
Jan 12, 2023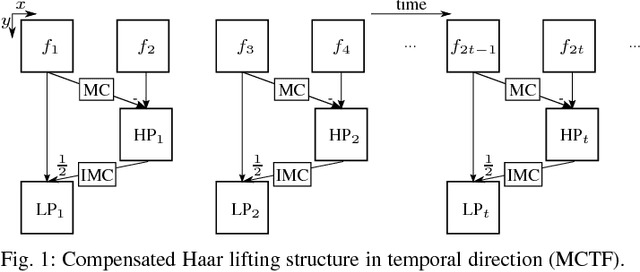
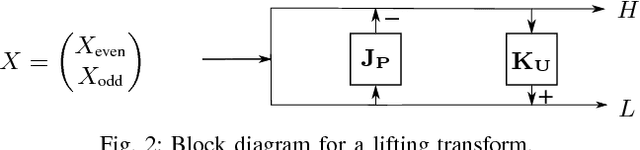
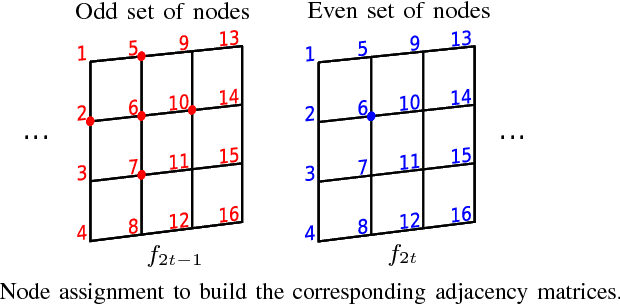
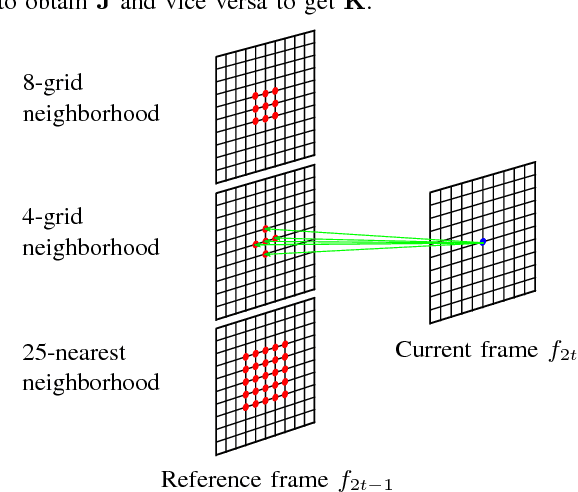
An efficient scalable data representation is an important task especially in the medical area, e.g. for volumes from Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Tomography (MRT), when a downscaled version of the original signal is needed. Image and video coders based on wavelet transforms provide an adequate way to naturally achieve scalability. This paper presents a new approach for improving the visual quality of the lowpass band by using a novel graph-based method for motion compensation, which is an important step considering data compression. We compare different kinds of neighborhoods for graph construction and demonstrate that a higher amount of referenced nodes increases the quality of the lowpass band while the mean energy of the highpass band decreases. We show that for cardiac CT data the proposed method outperforms a traditional mesh-based approach of motion compensation by approximately 11 dB in terms of PSNR of the lowpass band. Also the mean energy of the highpass band decreases by around 30%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge